5 Cloud Deployment Models: Learn the Differences
The demand for cloud computing has given rise to different types of cloud deployment models. These models are based on similar technology, but they differ in scalability, cost, performance, and privacy.
It is not always clear which cloud model is an ideal fit for a business. Decision-makers must factor in computing and business needs, and they need to know what different deployment types can offer.
Read on to learn about the five main cloud deployment models and find the best choice for your business.
What is Cloud Deployment?
Cloud deployment is the process of building a virtual computing environment. It typically involves the setup of one of the following platforms:
- SaaS (Software as a Service)
- PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
Deploying to the cloud provides organizations with flexible and scalable virtual computing resources.
A cloud deployment model is the type of architecture a cloud system is implemented on. These models differ in terms of management, ownership, access control, and security protocols.
The five most popular cloud deployment models are public, private, virtual private (VPC), hybrid, and community cloud.
Learn more about IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in cloud computing by referring to our comparison article IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS.
Comparison of Cloud Deployment Models
Here is a comparative table that provides an overview of all five cloud deployment models:
| Public | Private | VPC | Community | Hybrid | |
| Ease of setup | Very easy to set up, the provider does most of the work | Very hard to set up as your team creates the system | Easy to set up, the provider does most of the work (unless the client asks otherwise) | Easy to set up because of community practices | Very hard to set up due to interconnected systems |
| Ease of use | Very easy to use | Complex and requires an in-house team | Easy to use | Relatively easy to use as members help solve problems and establish protocols | Difficult to use if the system was not set up properly |
| Data control | Low, the provider has all control | Very high as you own the system | Low, the provider has all control | High (if members collaborate) | Very high (with the right setup) |
| Reliability | Prone to failures and outages | High (with the right team) | Prone to failures and outages | Depends on the community | High (with the right setup) |
| Scalability | Low, most providers offer limited resources | Very high as there are no other system tenants | Very high as there are no other tenants in your segment of the cloud | Fixed capacity limits scalability | High (with the right setup) |
| Security and privacy | Very low, not a good fit for sensitive data | Very high, ideal for corporate data | Very low, not a good fit for sensitive data | High (if members collaborate on security policies) | Very high as you keep the data on a private cloud |
| Setup flexibility | Little to no flexibility, service providers usually offer only predefined setups | Very flexible | Less than a private cloud, more than a public one | Little flexibility, setups are usually predefined to an extent | Very flexible |
| Cost | Very Inexpensive | Very expensive | Affordable | Members share the costs | Cheaper than a private model, pricier than a public one |
| Demand for in-house hardware | No | In-house hardware is not a must but is preferable | No | No | In-house hardware is not a must but is preferable |
The following sections explain cloud deployment models in further detail.
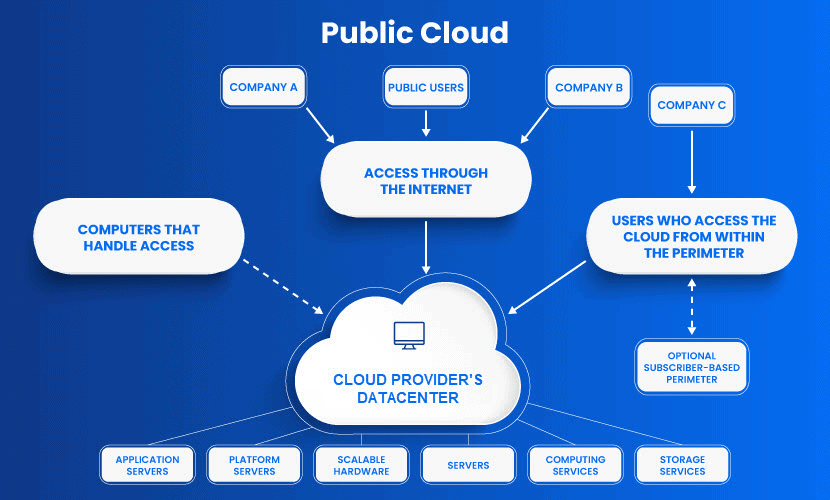
Public Cloud
The public cloud model is the most widely used cloud service. This cloud type is a popular option for web applications, file sharing, and non-sensitive data storage.
The service provider owns and operates all the hardware needed to run a public cloud. Providers keep devices in massive data centers.
The public cloud deliverynmodel plays a vital role in development and testing. Developers often use public cloud infrastructure for development and testing purposes. Its virtual environment is cheap and can be configured easily and deployed quickly, making it perfect for test environments.
Advantages of Public Cloud
Benefits of the public cloud include:
- Low cost: Public cloud is the cheapest model on the market. Besides the small initial fee, clients only pay for the services they are using, so there is no unnecessary overhead.
- No hardware investment: Service providers fund the entire infrastructure.
- No infrastructure management: A client does not need a dedicated in-house team to make full use of a public cloud.
Disadvantages of Public Cloud
The public cloud does have some drawbacks:
- Security and privacy concerns: As anyone can ask for access, this model does not offer ideal protection against attacks. The size of public clouds also leads to vulnerabilities.
- Reliability: Public clouds are prone to outages and malfunctions.
- Poor customization: Public offerings have little to no customization. Clients can pick the operating system and the sizing of the VM (storage and processors), but they cannot customize ordering, reporting, or networking.
- Limited resources: Public clouds have incredible computing power, but you share the resources with other tenants. There is always a cap on how much resources you can use, leading to scalability issues.
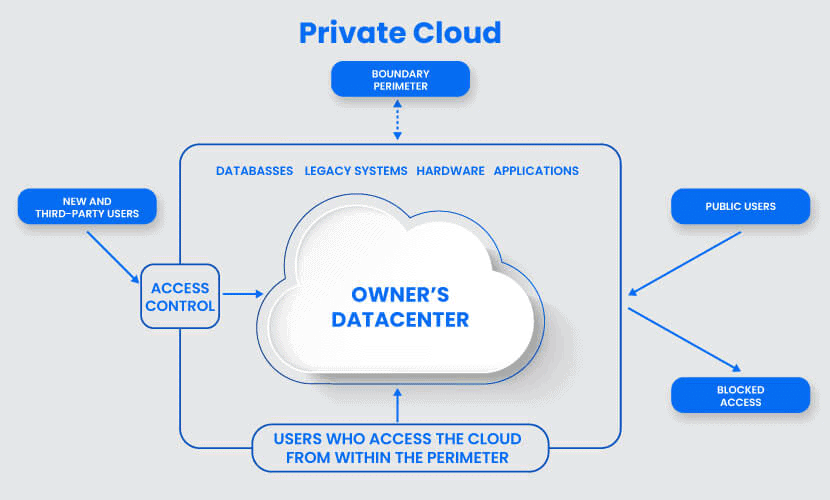
Private Cloud
Whereas a public model is available to anyone, a private cloud belongs to a specific organization. That organization controls the system and manages it in a centralized fashion. While a third party (e.g., service provider) can host a private cloud server (a type of colocation), most companies choose to keep the hardware in their on-premises data center. From there, an in-house team can oversee and manage everything.
The private cloud deployment model is also known as the internal or corporate model.
Advantages of Private Cloud
Here are the main reasons why organizations are using a private cloud:
- Customization: Companies get to customize their solution per their requirements.
- Data privacy: Only authorized internal personnel can access data. Ideal for storing corporate data.
- Security: A company can separate sets of resources on the same infrastructure. Segmentation leads to high levels of security and access control.
- Full control: The owner controls the service integrations, IT operations, rules, and user practices. The organization is the exclusive owner.
- Legacy systems: This model supports legacy applications that cannot function on a public cloud.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
- High cost: The main disadvantage of private cloud is its high cost. You need to invest in hardware and software, plus set aside resources for in-house staff and training.
- Fixed scalability: Scalability depends on your choice of the underlying hardware.
- High maintenance: Since a private cloud is managed in-house, it requires high maintenance.
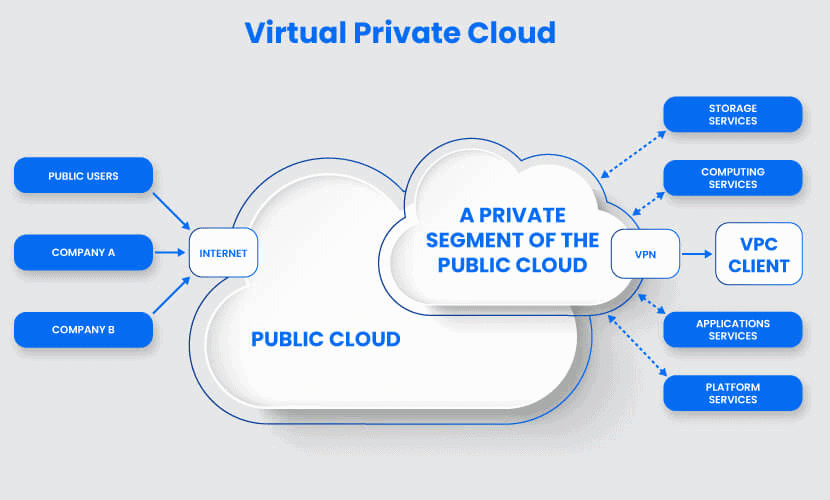
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
A VPC customer has exclusive access to a segment of a public cloud. This deployment is a compromise between a private and a public model in terms of price and features.
Access to a virtual private platform is typically given through a secure connection (e.g., VPN). Access can also be restricted by the user’s physical location by employing firewalls and IP address whitelisting.
See phoenixNAP’s Virtual Private Data Center offering and contact our representatives. To learn more about VDCs, refer to our article What is a Virtual Data Center?
Advantages of Virtual Private Cloud
Here are the positives of VPCs:
- Cheaper than private clouds: A VPC does not cost nearly as much as a full-blown private solution.
- More well-rounded than a public cloud: A VPC has better flexibility, scalability, and security than what a public cloud provider can offer.
- Maintenance and performance: Less maintenance than in the private cloud, more security and performance than in the public cloud.
Disadvantages of Virtual Private Cloud
The main weaknesses of VPCs are:
- It is not a private cloud: While there is some versatility, a VPC is still very restrictive when it comes to customization.
- Typical public cloud problems: Outages and failures are commonplace in a VPC setup.
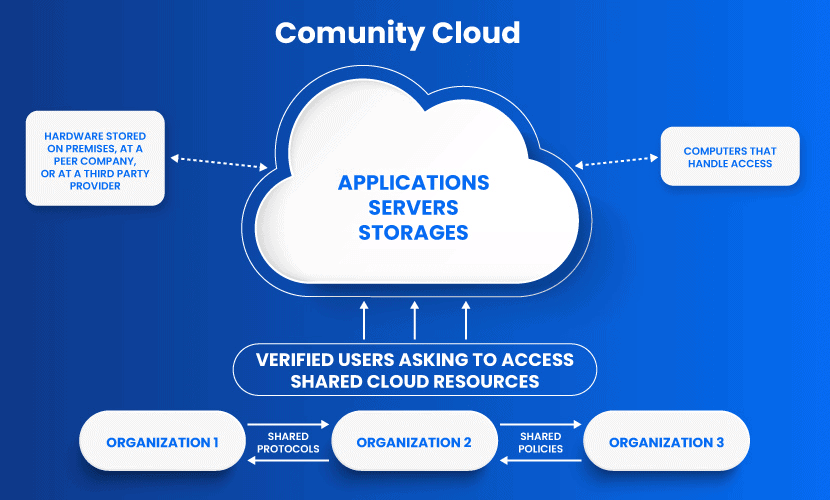
Community Cloud
The community cloud deployment model operates as a public cloud. The difference is that this system only allows access to a specific group of users with shared interests and use cases.
This type of cloud architecture can be hosted on-premises, at a peer organization, or by a third-party provider. A combination of all three is also an option.
Typically, all organizations in a community have the same security policies, application types, and legislative issues.
Advantages of Community Cloud
Here are the benefits of a community cloud solution:
- Cost reductions: A community cloud is cheaper than a private one, yet it offers comparable performance. Multiple companies share the bill, which additionally lowers the cost of these solutions.
- Setup benefits: Configuration and protocols within a community system meet the needs of a specific industry. A collaborative space also allows clients to enhance efficiency.
Disadvantages of Community Cloud
The main disadvantages of community cloud are:
- Shared resources: Limited storage and bandwidth capacity are common problems within community systems.
- Still uncommon: This is the latest deployment model of cloud computing. The trend is still catching on, so the community cloud is currently not an option in every industry.
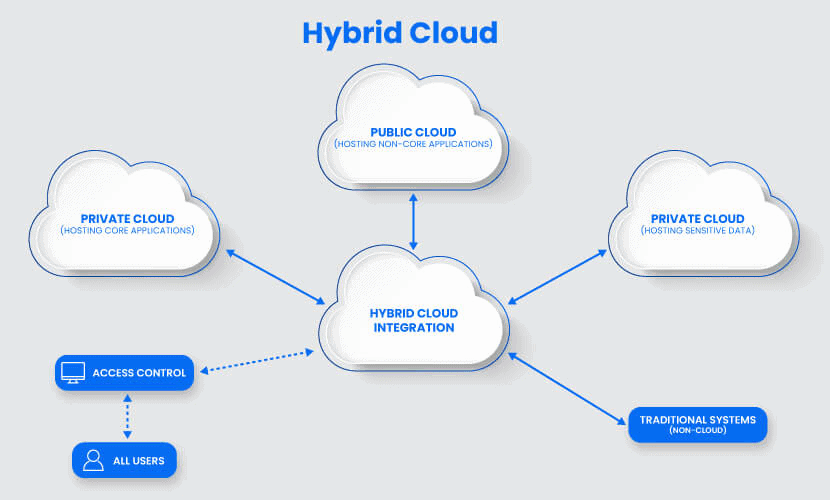
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is a combination of two or more infrastructures (private, community, VPC, public cloud, and dedicated servers). Every model within a hybrid is a separate system, but they are all a part of the same architecture.
A typical deployment model example of a hybrid solution is when a company stores critical data on a private cloud and less sensitive information on a public cloud. Another use case is when a portion of a firm’s data cannot legally be stored on a public cloud.
The hybrid cloud model is often used for cloud bursting. Cloud bursting allows an organization to run applications on-premises but “burst” into the public cloud in times of heavy load. It is an excellent option for organizations with versatile use cases.
Discover improved performance, flexibility, enhanced security, and optimize your IT spending with phoenixNAP’s Hybrid Cloud Hosting.
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud
Here are the benefits of a hybrid cloud system:
- Cost-effectiveness: A hybrid solution lowers operational costs by using a public cloud for most workflows.
- Security: It is easier to protect a hybrid cloud from attackers due to segmented storage and workflows.
- Flexibility: This cloud model offers high levels of setup flexibility. Clients can create custom-made solutions that fit their needs entirely.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud
The disadvantages of hybrid solutions are:
- Complexity: A hybrid cloud is complex to set up and manage as you combine two or more different cloud service models.
- Specific use case: A hybrid cloud makes sense only if an organization has versatile use cases or need to separate sensitive and non-sensitive data.
How to Choose Between Cloud Deployment Models
To choose the best cloud deployment model for your company, start by defining your requirements for:
- Scalability: Is your user activity growing? Does your system run into sudden spikes in demand?
- Ease of use: How skilled is your team? How much time and money are you willing to invest in staff training?
- Privacy: Are there strict privacy rules surrounding the data you collect?
- Security: Do you store any sensitive data that does not belong on a public server?
- Cost: How much resources can you spend on your cloud solution? How much capital can you pay upfront?
- Flexibility: How flexible (or rigid) are your computing, processing, and storage needs?
- Compliance: Are there any notable laws or regulations in your country or industry? Do you need to adhere to compliance standards?
Answers to these questions will help you pick between a public, private, virtual private, community, or hybrid cloud.
Typically, a public cloud is ideal for small and medium businesses, especially if they have limited demands. The larger the organization, the more sense a private cloud or Virtual Private Cloud starts to make.
For bigger businesses that wish to minimize costs, there are compromise options like VPCs and hybrids. If your niche has a community offering, that option is worth exploring.
Control your cloud costs! CloudAdmin tools let you monitor all your cloud costs and identify areas for optimization. Sign Up Here!
Invest Wisely in Enterprise Cloud Computing Services
Each cloud deployment model offers a unique value to a business. Now that you have a strong understanding of every option on the market, you can make an informed decision and pick the one with the highest ROI.
If security is your top priority, learn more about Data Security Cloud, the safest cloud option on the market.