Bare Metal Cloud vs IaaS: What are the Differences?
Do you feel your business would improve from having dedicated resources available on demand?
If your critical workloads need full processing capacity that you don’t usually achieve with virtualization, consider using a bare metal cloud server. But before we get to that, let’s start at the beginning.
To understand the differences between all the server hosting options available to you, first, you need to understand what is possible. Below are two definitions of the most basic types of server environments:
What is a Dedicated Server?
A dedicated server is a physical storage device capable of storing operating systems (OS), hypervisor layers, and virtual servers. It’s tangible and acts as the hardware component in housing the above software constructs needed to run programs or devices called “clients.” Since they are physical technology, companies need to store them on site.
In addition to inherent storage costs, dedicated servers are the most expensive server hosting option for business. However, dedicated servers’ high cost reflects its power. Companies that steadily demand high server capacity use dedicated servers for their unparalleled performance.
Lastly, these types of servers are single-tenant environments, meaning only one client can access the hardware. Privacy needs, price, and storage space are considerations one must take into account before deciding if dedicated servers are for them.
What is a Virtual Server?
A virtual server, also known as a virtual machine, is a software-defined server that runs on top of a physical machine, such as a dedicated server.
This definition means virtual servers still require physical machines to run on. However, it allows for multi-tenant environments. You still get single-tenant access to your virtual resources but hardware resources are divided among many virtual machines.
The main benefits of virtual machines are its low-cost and flexibility. Furthermore, virtual server resources can often be rented on a pay-as-you-go model, meaning you pay for what you use.
Electing to rent a virtual server has become popular among businesses that don’t require the best performance or highest capacity servers, as virtual servers are more affordable and offer better value through varying levels of performance configurations. For businesses with variable workloads, renting cloud servers allow them to scale according to their needs.
Now that you have a fundamental understanding of dedicated and virtual servers, it will be easier to discern more advanced variations of these services, such as bare metal servers, infrastructure-as-a-service, and bare metal cloud.
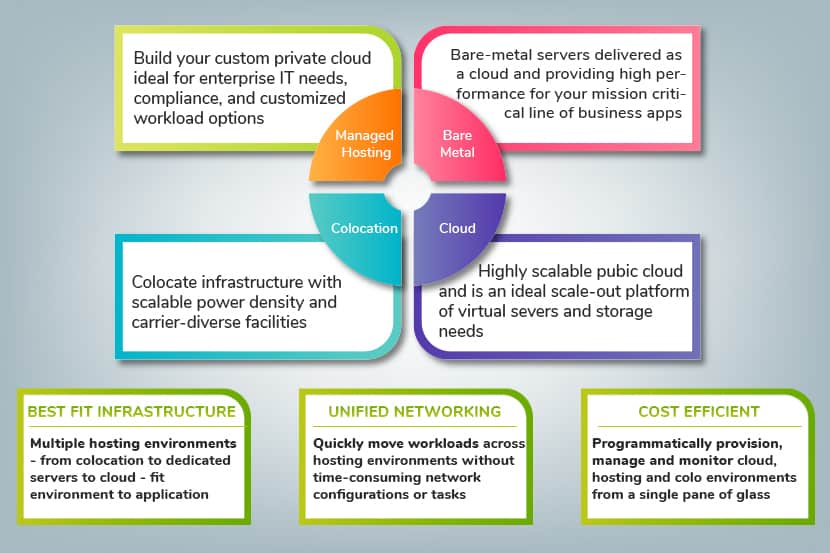
What is a Bare Metal Server?
Dedicated servers and bare metal servers are very similar. Both of these servers are single-tenant machines that give users complete access to the underlying hardware. This access is possible because they do not use a hypervisor layer to create separate virtual machines (VM) on the server. Instead, the server eliminates the need for layers by installing the operating system directly on the server. The result is some of the best performance on the market.
These servers also allow for the configuration of its processor, storage, and memory, which isn’t shared. On VMs, this is not the case, as the providers control the hardware. With both of these server types, users needn’t worry about their performance suffering, as their hardware is used to power their web hosting or applications solely.
On the contrary, the difference between a dedicated and bare metal server comes down to the quality of the hardware components and the flexibility of contracts.
Bare metal servers provide configurations with top-of-the-line hardware products such as newest generation processors, best-in-class random access memory (RAM), and NVMe solid-state drives (SSDs) with lightning-fast load times. Whereas, dedicated servers do not.
In terms of contracts, bare metal servers also offer more flexibility in billing. Use them for a dramatically shorter time-period than dedicated servers, where you only pay for what you use. You can even run a bare metal server on a per-hour billing model.
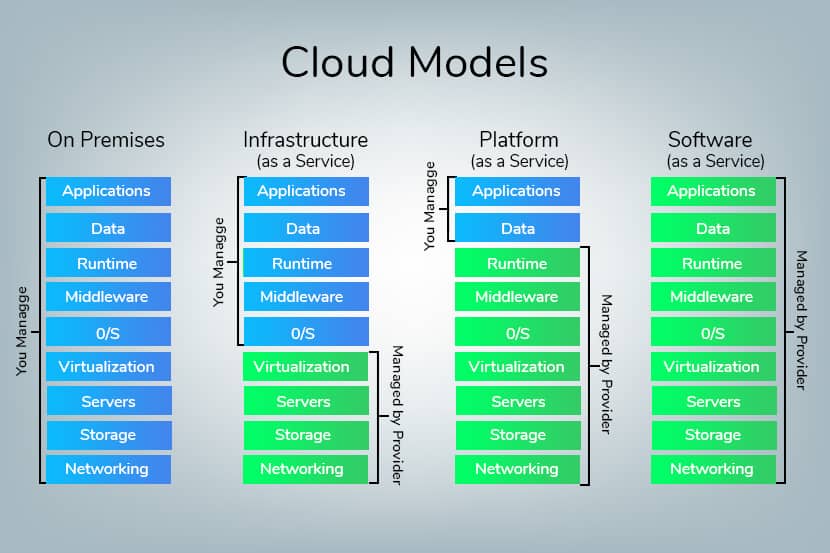
What is Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS)?
Infrastructure-as-a-service is a type of cloud service that runs on a distributed environment composed of multi-tenant, virtualized servers.
Businesses can thus avoid having to buy and manage their own servers in lieu of renting a resource directly from a cloud computing service provider. By renting based on the resource, companies can rent and pay strictly for what they use as long as they need. Once you make a purchase, all that’s required is for the company to install, configure, and manage their operating systems and applications, while the service provider manages the server infrastructure.
In choosing this option, businesses can access their web hosting from a virtual server without having to own the physical hardware.
Learn more about IaaS in our comparison article IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS
Bare Metal Cloud & IaaS: What are the differences?
Cloud technology breaks down into three main categories: Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), software-as-a-service (Saas), and platform-as-a-service (PaaS). Of these three, bare metal cloud is a subset of IaaS cloud services.
With bare metal cloud servers, users can possess the power and security of dedicated server hardware with the networking connectivity and storage of a data center. Even though the bare metal cloud is an IaaS product, it gives more flexibility to the end-user by allowing them to manage their own hypervisor or OS installed on the server.
Ultimately, bare metal cloud gives the end-user the best of both worlds: the flexibility, scalability, and predictability of a cloud service and the hardware control of a dedicated server by managing the configuration and licensing of software on the machine.
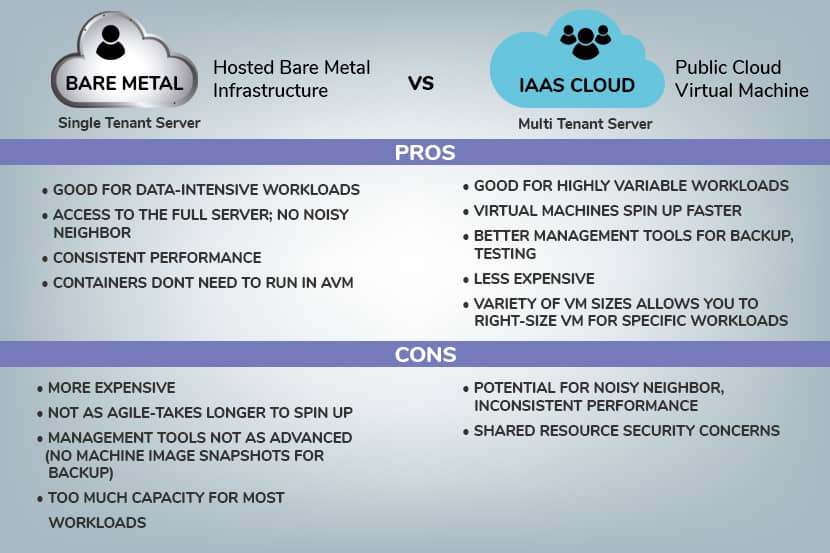
Bare Metal Cloud vs IaaS
As mentioned earlier, bare metal cloud is a subset of IaaS. Although they are both cloud services, they provide different levels of offerings. IaaS can be defined as the provision of virtual resources; whereas, bare metal provisioning gives access to virtual resources as well as dedicated servers.
In both scenarios, you have access to a server where you can install your OS and applications of choice. Where they differ is you have no control over the infrastructure on IaaS. Instead, the service provider manages it. Your business only has access to the confines of a virtual environment.
On the other side of the coin, bare metal cloud provisions your business with a fully dedicated server for you to configure how you wish. You receive control over the full server stack and can install hypervisors and VMs at your discretion.
How Do Bare Metal Servers Work in the Cloud?
As a private cloud hosting solution, you will have access to a private environment that provides the same accessibility as a public cloud but with more control and performance over virtual machine solutions. Moreover, because the servers are dedicated, you won’t experience restrictions of resources due to other tenants’ workloads. Your business will have full processing capacity you can’t get with virtualization.
If compliance measures or processing power restricts your organization, then this is an option for you. This environment offers complete control over the physical resources of a server through isolation.
Latency sensitive business applications, gaming, media streaming, and real-time analytics are some examples of intensive workloads where this service can help to achieve smooth operation of business continuity.
The History of Server Technology
In the past, dedicated servers used to reign as the most powerful server hosting solution due to its unrivaled performance and lack of contention. However, all that power was expensive to host and took a lot of effort to maintain because users had to manually install operating systems on the servers and then layer on specific application software to perform desired tasks.
With the invention of cloud or virtualization services, businesses began to see a competitive alternative to hosting dedicated servers on-site or on rented racks in data centers. Companies that didn’t require the best performance and needed quicker scalability chose cloud computing services for more cost-effective server hosting.
These cloud services were able to cut costs through the process of virtualization. How? They used software to make a single piece of hardware to appear to be many; cloud service providers could make operating systems run multiple instances of virtual machines by installing hypervisors. And each instance of a virtual machine appeared to be its own computer. This innovation allowed for service providers to support multiple customers on one physical server; hence, the multi-tenant, virtual server was born.
This innovation led to the selling of infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), which is the provisioning of storage, networking, and computing power for sale on an on-demand basis.
Even though the migration to cloud services had begun, the market still required the benefits of owning and operating single-tenant, physical servers. As stated earlier, bare metal servers are not an entirely new creation in server hosting. Their predecessor, the dedicated server, was reinvented to continue to facilitate a need for absolute control, security, customization, and access over company servers. That is why bare metal servers are still popular commodities.
With both dedicated server hardware and cloud services having their strengths and weaknesses, bare metal cloud servers are a more recent development in server technology that acts as a hybrid to bridge the forces of the two without compromise.
Benefits of Bare Metal Cloud Servers
Operational Costs vs. Capital Expenditure
In IT, there are two ways to go about purchasing servers. Either you can buy servers outright and own them; this is called capital expenditure. Conversely, you can purchase server performance on an on-going basis, also known as operational costs.
The problem with capital expenditure is it is hard to judge the IT needs of your business a couple of years from today. This inexactness can lead to an unwise decision of over-buying capacity, which takes from your business’ overhead.
Now, with operational costs, your business can enlist an IaaS service provider, which provides maintenance, updates its hardware catalog with greater rapidity, and can update your business with new server hosting capabilities as needed. Selecting this option gives your business the ability to meet its IT needs while preserving its capital.
If you are looking for different server options for your business, you might find our buying guide for Small Business Servers useful.
Better Overall Performance
With bare metal servers, you can customize hardware to your unique needs. These do not incur the overhead of VM platforms, so the total response times are increased. Service performance is high in a hosted environment that combines dedicated to infrastructure as a service. Besides, more processing power is available because no type (1,2) of hypervisor is needed. Another advantage is that other tenants’ workloads do not impact performance.
Hybrid Deployment
As part of an enterprise-level infrastructure, bare metal is essential for a successful hybridization of a cloud solution. A bare-metal instance can be deployed as part of hybrid cloud infrastructure to protect the most sensitive or intensive data. Consider mobile gaming or advertising platforms that deal with large volumes of data that require high-performance scalability. In this case, bare metal is the center of the infrastructure.
These environments are also the central hub for business analytics, client information, and other types of sensitive data. In addition to this, this infrastructure delivery model provides the capability to shift workloads between multiple connected environments.
Learn about phoenixNAP's Hybrid Cloud Computing Solution and why it is the best choice for your business.
Lower Big Data Transfer Costs
If you are handling bandwidth-heavy or data-intensive workloads, you need a solution that keeps your IT infrastructure costs at the minimum while delivering excellent performance. Bare-metal cloud or dedicated server solutions offer a more economical approach to transferring outbound data, which helps you lower your data transfer and bandwidth costs.
Although managed service plans with hyperscale data center cloud providers are usually cheaper than single-tenant solutions, they do not always help you lower your operational costs. Cloud providers typically charge more for bandwidth and traffic. Bare metal service plans offer better prices in that respect and minimize your overhead.
If you have software that can leverage specific hardware features, bare metal further helps you optimize your costs in the cloud. By allowing for custom configurations tailored to your needs, they help you improve your performance or density. You can optimize your infrastructure for specific features to ensure it meets your needs regarding performance. Optimization enables you to do more with less, directly bringing operational cost savings.
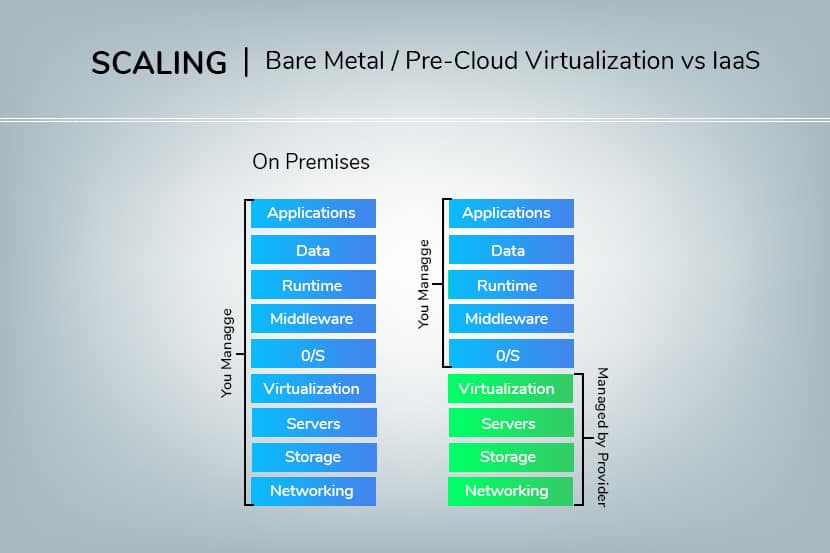
Dedicated Resources, Bare Metal vs. Virtual Machines
As mentioned earlier, dedicated hardware and bare metal software resources are possibly the most significant advantage. With a dedicated server, you do not have to share storage, bandwidth, or network connection with other tenants on the same platform. You can also expect improved security and privacy, as your big data is isolated from other users.
This environment benefits companies that handle users’ personal information or data-intensive workloads, which require constant and predictable resources. Such an environment provides superior processing over VMs alongside better network performance.
Dedicated servers are excellent for game servers, enormous relational databases, data analytics, rendering, transcoding, software development, and website hosting. It is also widely used for machine learning and artificial intelligence workloads, or enterprise resource planning applications. The one thing in common with everything just mentioned is they are all data-heavy.
In a virtual setting, the “noisy neighbor” issue occurs as VMs fight for server resources that disturb these data-heavy loads. Dedicated hardware also offers the same flexibility, efficiency, and scalability from VM clouds without the setbacks of shared resources.
You can configure dedicated servers to your exact specifications. You can select the amount of cloud storage, RAM, and the processor that fits your needs. It ranges from a moderately powerful to a very powerful machine on the market with vast amounts of memory. Because of this, you can make a dedicated server the most powerful hosting option. In addition to customized configuration, you can use any bare metal operating system you like or go with a control panel add-on or different software options.
Cloud Security and Compliance
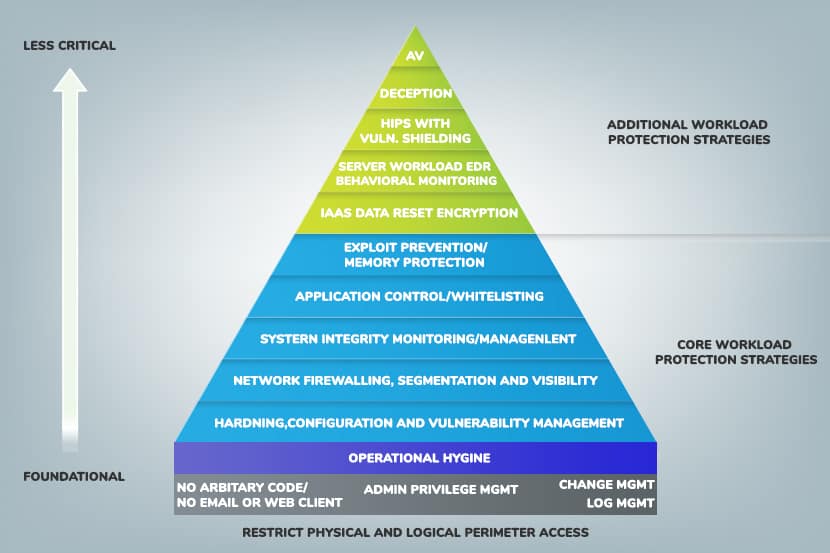
As a single-tenant environment, bare metal hosting addresses data protection and compliance concerns better than shared or virtualized platforms. They provide improved data and application performance, without compromising on security.
Without virtualization, the overhead of a hypervisor is gone, which increases performance. Most public cloud offerings and virtualized environments pose security and compliance risks to organizations. With the single-tenant platform committing resources to a single user, there are no more worries. If you need to follow strict industry regulations, virtual environments may lead to security issues.
To adequately protect their sensitive files and their clients’ data, businesses need to understand industry standards and security requirements.
Bare metal servers are configurable according to a specific organization’s needs, which is why they are an excellent option for regulated workloads.
Business Performance Advantages
Now that you know the significant benefits of bare metal servers let us find out if it is the right choice for you.
With the right server, you start with a blank slate ready to customize to fit your computing needs.
Large and growing businesses with massive traffic or large resource requirements benefit from a bare metal environment. It is also ideal for regulated industries or public sector companies that need enhanced data security. Law firms, medical offices, and other organizations that have strict security and compliance standards also benefit from the private cloud.
The level of data control and security cannot is incomparable to other forms of cloud computing. Overall, bare metal is the optimal solution where customization and resources are required while still maintaining the same flexibility and accessibility as the cloud.
Bare Metal Cloud and Containers
Bare metal cloud is capable of running containers as well. Instead of installing virtual machines on the server, deploy containers.
Containers take up less overhead than VMs. This efficiency is due to a container’s ability to isolate your application from wherever you are running it. Therefore, instead of installing a weighty VM, you can install only what you need to run your application in your container and do away with the rest of the guest operating system.
The industry trend is moving away from VMs and more towards containers because of their efficiency. New VMs always need to copy an OS and its entire configuration when established fully. Containers run on their own init processes, filesystems, and network stacks that are virtualized on top of VMs or host OS. Because they share the OS kernel and use identical libraries, they use less memory.
Bare Metal Cloud and Cloud-Native Infrastructure
The industry trend used to dictate introducing cloud-native applications on virtual machines by deploying Kubernetes. However, there is some complexity in doing so. Therefore, to simplify its deployment, many are using a bare metal cloud-native architecture to underpin the cloud-native technology, calling it Kubernetes bare metal. By doing this, no virtualization layer is needed in the cloud stack. Cloud-native applications deploy in containers directly on the bare metal cloud. The result is drastically less overhead, more substantial total cost of ownership (TCO) savings, fewer bottlenecks due to no need for guest OS, and radical simplification of network implementation.
The Unique Nature of Bare Metal Management
Bare metal providers offer cloud management interface consoles and command-line interfaces. PhoenixNAP’s Client Portal (PNCP), for example, provides a management interface that allows for primary data storage management and deployment. It offers automated API-driven server deployments and lets you streamline activities such as rebooting servers, upgrading network storage, DNS setup, and identity and access management. In addition to this, it lets you adjust security settings through Role-based Access Control (RBAC) features and two-factor authentication.
Administrators can use these control panels to perform a reset and power cycle, which is impossible with VM clouds. Once you get used to managing your own resources, you will not want to go back to a VM environment.
Going bare-metal is almost like regressing to computing days of the past; only it combines the best of both worlds. It blends a consistent performance computing environment and cloud-like flexibility into an ideal private cloud solution.
Backup, Restore, and Recovery
Bare Metal Backup & Restore allows your IT team to recreate data from scratch on a different system and ensure business continuity in the event of a catastrophic failure such as floods, fires, and other natural disasters.
The recovery and restore solutions, such as Carbonite Availability, follow an automated process with little human interaction, which is why they are fast and easy to set up. The physical hardware where the system is recovered without file-formats partitions or operating systems because the bare metal backup will recover all of these.
Cloud disaster recovery is quicker than a manual backup and is almost error-free. Recovery saves a lot of time for IT administrators who can spend their time backing up other systems from a catastrophic failure. Some recovery solutions enable incremental backups, which also saves storage space and bandwidth. Through the assistance of snapshots, ‘recovery and restore’ can recover to the last backup point or any available previous backup point.

Imagine a scenario in which you need to restore a significant amount of data from your offsite local data backup.
While having a local backup is a recommended best practice to ensure data availability, specialized cloud recovery solutions help you retrieve your data in a matter of minutes.
Storing data in the secure cloud has several advantages over traditional solutions. The primary benefit is that your data stores in a purpose-built data center facility with advanced security systems. In addition to this, using a third-party data center for data backup and recovery enables you to leverage improved internet speed instead of being dependent on global internet traffic.
Another way to think of it is to imagine sharing a suitcase with your family on your next flight somewhere. Each member of your family adds clothes and things to the bag, which becomes heavy and cluttered.
Next, imagine going through airport security with that single large bag and being asked for your passport, which you buried somewhere in that bag. Think of a dedicated server as having your o individual bag for your family trip, making it easier for you to sort through your things to find that missing passport.
Why Make the Move from Dedicated Servers to Cloud Service?
The move from dedicated servers to the cloud and now to bare metal cloud comes down to cost and usage scenarios. Dedicated servers are fixed costs that are typically used consistently for months or years at a time. However, when companies need a little extra performance for a shorter duration, they aren’t looking to spend extravagantly on new dedicated servers, especially for things like application testing or handling busy traffic periods.
Instead, companies are more likely to mitigate costs by enlisting the power of a cloud service for a shorter duration, where they only pay for what they use. This level of cost-efficiency is what spurs companies to adapt from owning physical hardware to using IaaS.
Bare Metal Cloud Service Providers Right For You?
If you’re looking for a cloud service where you retain control of your server environment, the bare metal cloud stands out as a feasible option.
From a cost perspective, this type of solution is billed monthly with no hidden fees; whereas, public cloud service typically presents a higher TCO, as you don’t know the costs associated with operating the server hardware.
Whether or not you choose to use the bare metal cloud is dependent on if you require high levels of processing power, additional security, root access to all systems on the server with more scalability than traditional dedicated servers, or traditional cloud services.
Ultimately the choice is yours when it comes to bare metal vs. cloud. You can select between VM cloud solutions that are easy to set up and usually more affordable. However, if you do not want performance issues or if you have resource-heavy loads, you can choose a bare-metal cloud provider.