Multi Cloud Security Best Practices
Multi-cloud is growing in popularity as companies continue to explore the benefits of working with more than one provider. While multi-cloud offers numerous advantages, relying on multiple vendors and clouds also increases the attack surface and overall risk. If a company wishes to keep assets and data safe, multi-cloud security must not be an afterthought.
This article is an intro to multi-cloud security and the unique challenges of this cloud computing approach. We also provide a list of best practices you can apply to design and maintain a safe multi-cloud setup.
What Is Multi-Cloud Security?
Multi-cloud security is a set of policies, strategies, and solutions a company relies on to ensure safety in a multi-cloud environment. This type of security enables a business to enjoy the benefits of multi-cloud without exposing data and assets to cyber threats.
The biggest challenge of multi-cloud security is managing and protecting environments from different cloud providers. Multiple vendors with varying features and rules complicate cloud security tasks, including:
- Ensuring consistent security controls.
- Setting up reliable access management.
- Identifying and responding to vulnerabilities.
- Maintaining a holistic view of security.
Typically, cloud providers are responsible for the safety of their clouds while the client is responsible for the security in the cloud. The provider’s job is to:
- Ensure the cloud infrastructure is secure, reliable, and up to date.
- Protect hosts and data centers.
- Provide clients with capabilities to protect data (multi-factor verification vectors, access management software, encryption tools, etc.).
A company deploying a multi-cloud is responsible for how the team uses and keeps data in each cloud infrastructure. The in-house team needs to:
- Design the general security architecture.
- Ensure operations comply with relevant laws and regulations.
- Define access rules and privileges.
- Handle cloud monitoring.
- Set up a backup strategy.
- Identify and respond to security incidents.
- Design safe deployment processes.
- Keep third-party tools up to date.
- Set up data loss prevention (DLP).
- Define steps for cloud disaster recovery.
Most companies rely on several roles to handle these tasks, spreading responsibilities between the CISO, DevOps team, and Security Operations Center (SOC).
Multi-Cloud Security Risks
The main risks of failing to set up proper multi-cloud security are:
- Losing sensitive data due to a lack of protection or human error.
- Paying monetary fines due to a failed compliance check.
- Hurting customer experience with prolonged downtime or poor app performance.
- Falling victim to malware that leads to a data breach.
- Allowing an unauthorized user to access internal data.
- Suffering a reputation hit as a result of losing private user data.
These dangers are common risks of using cloud computing in general, whether in a single or multi-cloud setup. However, a company must protect a larger attack surface in a multi-cloud, and the sheer complexity makes issues more likely. Below are the main challenges that make multi-cloud riskier than a single cloud:
- The team must configure, secure, and manage more than one infrastructure.
- Every platform requires ongoing maintenance.
- Each provider has unique security policies, controls, and granularity.
- An attacker has more ways to infiltrate the setup.
- The monitoring must account for the full scope of the cloud deployment.
- The team must connect and integrate various services from different vendors.
Best Practices in Achieving Multi-Cloud Data Security
Companies require a sound security strategy to ensure multi-cloud does not lead to vulnerabilities. Below are 11 multi-cloud security best practices that can help you safely spread workloads across multiple providers and environments.
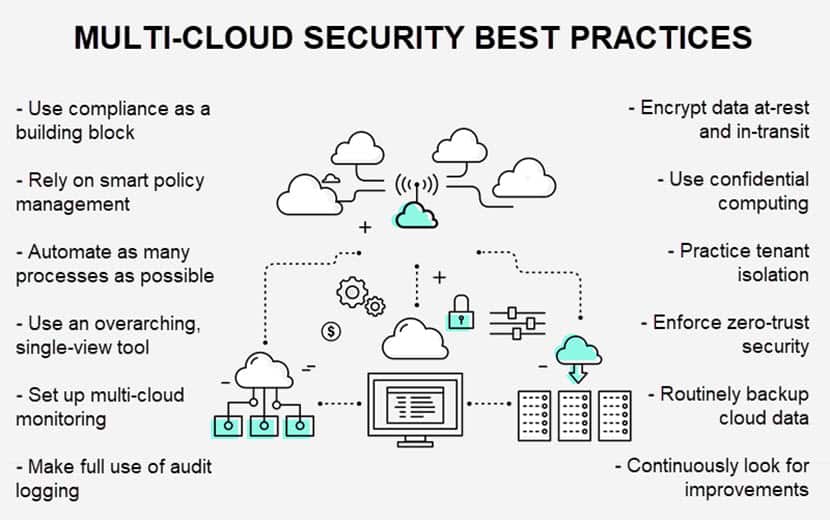
Build the Security Strategy around Compliance
The first step towards achieving compliance in a multi-cloud is to know the standards and regulations that apply to your business. Common examples of regulations companies need to account for are data privacy laws (namely GDPR and CPA), HIPAA, and PCI.
Regulations apply to specific industries and locations, so know what your multi-cloud needs to adhere to before you start deploying. Once you know what the expectations are, use the legal requirements to:
- Outline the lifecycle of relevant data.
- Define security controls.
- Set up access management.
- Classify all cloud data.
- Organize adequate storages.
Remember that each cloud platform has different compliance features and certifications. You might even run separate workloads with varying compliance rules on a single cloud. Consider using an automated tool to continuously audit compliance across clouds and generate reports on potential violations.
Smart Policy Management
Companies should develop a set of security policies to enforce on all cloud environments and simplify security operations. A policy defines:
- Acceptable types of data.
- Cloud ownership.
- Authentication and access rules.
- Cloud workload security and gateways.
- Security analytics.
- Regulation rules and current compliance status.
- Cloud migration protocols.
- Threat modeling, prioritization, and intelligence.
- A response plan for each attack type.
While some incompatibilities between environments are common, using a standardized policy as a starting point will:
- Speed up configuration and deployment.
- Reduce the risk of oversights and human error.
- Ensure consistency across the multi-cloud.
If you are running the same operations in multiple clouds, you should synchronize policies. For example, when using multi-cloud to ensure availability, both clouds should have the same security settings. The team should use a tool to synchronize settings between the two providers and create a policy with generic definitions that apply to both clouds.
Leverage Automation
A significant risk factor in multi-cloud security is human error. By automating as many tasks as possible, a business can:
- Reduce the likelihood of employees making mistakes.
- Add agility to the team.
- Speed up cloud-related processes.
- Ensure consistency across environments.
Automation should play a vital role in multi-cloud security. For example, each new container or virtual machine can go through automatic security scans. Another way to use automation is to run continuous checks that test security controls.
Adopting DevSecOps is an excellent way for a company to start thinking about the role of automation in cloud computing security. DevSecOps treats security as a core consideration instead of an afterthought, an approach ideal for keeping multi-cloud safe.

Simplify the Multi-Cloud Tool Stack
Instead of relying on a mix of provider’s native tools and third-party solutions, you should invest in a single, overarching tool that provides seamless security across the multi-cloud. Otherwise, you risk:
- Poor integrations that result in security gaps.
- Higher chance of human error.
- Hiring more staff than you require.
- Burdening the team with too much maintenance.
Ensure your tool of choice can:
- Seamlessly integrate with different cloud services.
- Scale alongside your apps and workloads.
- Provide real-time updates to data activity.
Also, your security tool should have a single pane of glass from which admins can manage apps and data across clouds. A single-view tool simplifies the sprawl and makes the security team more effective.
Set Up Multi-Cloud Monitoring
A multi-cloud requires robust monitoring that consolidates events, logs, notifications, and alerts from different platforms into one location. Another vital feature is to have a tool that can either automatically solve issues or provide guidance during remediation.
Beyond consolidation and automatic fixes, your monitoring tool should also:
- Be scalable to meet the growing cloud infrastructure and data volumes.
- Offer continuous real-time monitoring.
- Provide context to all alerts.
- Allow the team to create custom notifications.
Make Full Use of Audit Logging
Audit logging documents all changes related to cloud tenants, including:
- The addition of new users.
- Access right granting.
- Login duration.
- User activity during the login.
Audit logs are crucial to multi-cloud security as this activity helps:
- Identify malicious behavior.
- Discover the breach before a cyberattack starts.
- Uncover code or cloud-related issues.
- Run operational troubleshooting.
Additionally, audit logs are official records in some industries, and companies can use logs to prove compliance to an auditor.
Rely on Data Encryption and Confidential Computing
Encryption is an effective method of protecting data, both on-premises and in the cloud. A multi-cloud security strategy should encrypt data both at rest and in transit:
- Encryption at rest protects stored data that is not moving through the network. If an intruder breaches the database, deciphering the data is impossible without the decryption key.
- Encryption in transit protects data while the information is moving through the network. If an intruder intercepts the data with a Man-in-the-Middle attack or eavesdropping, the data remains safe.
In addition to securing both still and moving data, you should also encrypt all scheduling, monitoring, and routing communications. Thorough encryption ensures the information about your infrastructure and apps stays secret.
Besides encrypting data at rest and in transit, a multi-cloud security strategy should also include confidential computing to ensure data does not become vulnerable while in use. In-use encryption provides total protection of cloud data by encrypting workloads during processing.
Practice Tenant Isolation
Tenant isolation is a simple and effective method to improve multi-cloud security. Tenant isolation requires the team to ensure that:
- Every app runs in a separate tenant.
- All environments (development, testing, staging, production, etc.) run within individual tenants.
For extra security and agility, you can also use landing zones. A landing zone allows the team to quickly set up a multi-tenant environment with a predefined baseline of access management, data security, governance, and logging rules.
Enforce the Principle of Least Privilege
Each employee should only have access to the resources necessary for that staff member to perform their role. This principle of least privilege serves several purposes:
- Isolate mission-critical and sensitive data.
- Reduce attackers’ ability to move laterally through the system if they hack an account.
- Help the business comply with data privacy and security laws.
Using the cloud provider’s native tools to control access is not a good idea in a multi-cloud. Solutions from different vendors work poorly together and create silos that increase risk. Instead, use a holistic tool that centralizes access controls across all clouds.
Be careful not to hinder the team with missing access rights or slow approval processes. Instead, create a simple and transparent process for assigning access rights that helps protect the multi-cloud without slowing down operations.
Routinely Backup Cloud Data
Regularly perform cloud backups of data and systems. Whether you decide to store backups in-house or in the cloud, you should follow several good practices:
- Use immutable backups to ensure attackers cannot encrypt or delete data even if they breach the multi-cloud.
- Backup data multiple times a day.
- Keep a separate backup for each cloud to simplify recoveries.
- Use zero-trust strategies to keep backups secure.
- Use a tool that continuously scans backups for malicious data.
In addition to backups, a multi-cloud security strategy also requires a disaster recovery plan. Design a plan that both restores data quickly and keeps services available on a reserve cloud.
Build a Culture of Continuous Improvements
Every multi-cloud security strategy must go through regular assessments to ensure the defenses keep up with the latest standards. To ensure security does not fall too far behind, a team should:
- Regularly check for software updates.
- Stay up with the latest cybersecurity trends by keeping an eye on how companies protect data and how criminals breach systems.
- Run regular vulnerability assessments, both with outsourced experts and on an in-house level.
- Ensure all third-party tools are up to date with the latest updates.
- Constantly look for new ways to make security more automated and efficient.
Use Security as a Building Block for Your Multi-Cloud Strategy
Any careful company must consider and account for security needs before starting the multi-cloud journey. Ensure security is the foundation of your strategy and create a multi-cloud that increases your flexibility without making you vulnerable to cyber threats.