What is an Edge Server and How Does it Work?
While edge servers perform the same functions as a traditional server, these devices do so from a non-traditional location. An edge server processes data physically close to the end-user, whether in a smart home, IoT-powered factory, hospital, or self-driving car. Running operations at the network's edge eliminates processing backlogs and distance lags, two prevalent issues of traditional servers.
This article offers an in-depth look into edge servers and the role these devices play in the current IT landscape. Read on to learn what edge servers are, how they work, and why these devices are a top choice for low-latency use cases.
What Is an Edge Server?
An edge server is a piece of hardware that performs data computation at the end (or "edge") of a network. Like a regular server, an edge server can provide compute, networking, and storage functions.
Edge servers process data physically close to the end-users and on-site apps, so these devices process requests faster than a centralized server. Instead of sending unprocessed data on a trip to and from a data center, these devices process raw data and return content to client machines. As a result, edge servers provide snappier performance, lower latency, shorter loading times.
There are two types of edge servers:
- Content delivery network (CDN) edge servers: A CDN edge server is a computer with cached versions of static content from an origin server (images, JavaScript files, HTML files, etc.). A company can deploy CDN edge servers at various points of presence (PoPs) across a content delivery network.
- Edge compute servers: This server type provides compute resources at the network's edge. While a CDN server only delivers static web content, an edge compute server provides functionalities needed for IoT apps.
Keep in mind that there is a difference between edge servers and devices. The term "edge device" refers to hardware that provides an entry point to a network (such as a router or switch).
Learn more about edge computing and see how placing workloads at the network's edge can boost performance in various use cases and settings.
Edge Server vs Origin Server
A CDN edge and origin server typically work in tandem to deliver content to end-users. The two devices have similar abilities, but they play different roles in the content-delivery process.
An origin server is a computer that runs programs for listening and responding to internet requests. Depending on the distance between the origin server and user, responses may come with a delay. The additional round-trip time (RTT) needed for establishing a secure internet connection using SSL/TLS can also increase latency.
A CDN edge server significantly reduces latency by sitting between the origin server and the requesting machine. By hosting static assets in a strategic location close to the client machine, an edge server speeds up the time it takes for a web resource to load.
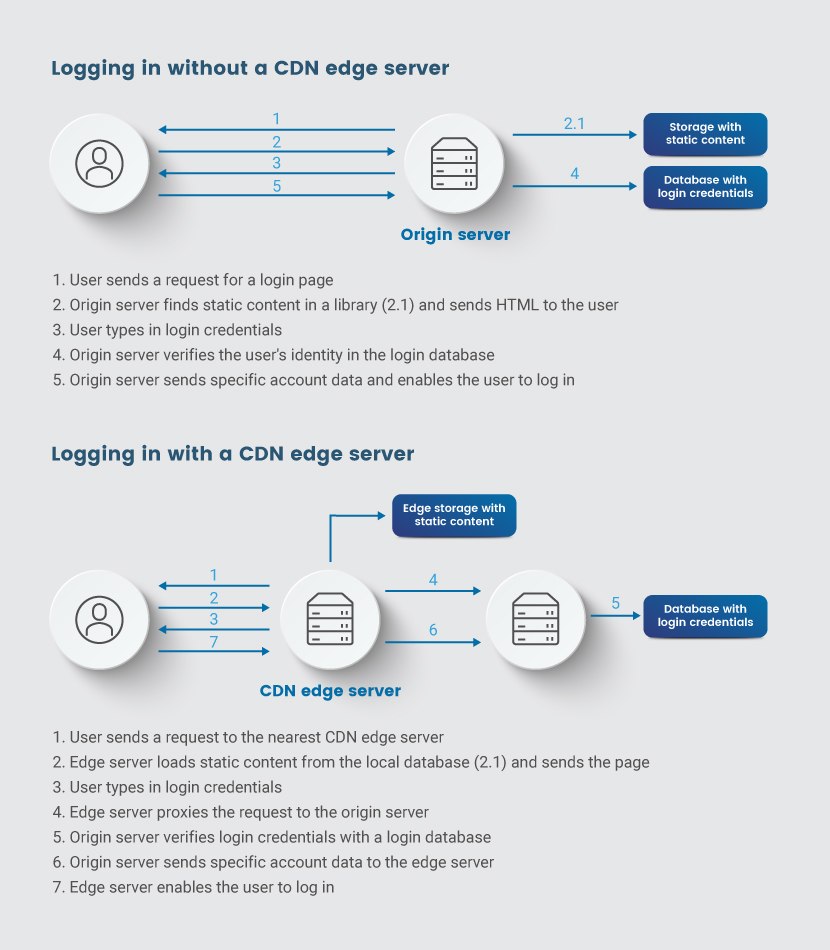
Here's an example of how an edge and origin server work together to serve up a login page:
- The user sends a request to access the login page.
- The CDN uses Anycast DNS to determine the closest CDN edge server and routes the request to that device.
- An edge server loads the static content and returns it to the user device without any bandwidth consumption by the origin server.
- Once the page renders, the user types in a username and password.
- The request for dynamic content travels to the edge server which then proxies the request back to the origin server.
- The origin server verifies the user's identity in the associated database and sends back specific account data.
Edge servers are not a replacement for origin servers (or vice versa). An origin server is vital when using a CDN server as it hosts operations that are unsafe for the edge. Good examples are databases of hashed client credentials used for authentication or vulnerable backends.
Edge Server vs Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the act of running a workload on a cloud, a software-defined environment created by a data center or server farm. Edge computing is the act of running a workload on an edge server, a piece of hardware that runs outside of a data center.
While different, edge and cloud computing are not mutually exclusive. An edge server can be a part of a cloud if you abstract its storage and computing resources. Also, both edge and cloud computing can use containers, software packages that can run on any cloud deployment model.
Our comparison of edge and cloud computing goes in-depth into the subject and explains the pros and cons of each computing model.
How Do Edge Servers Work?
An edge server sits between and interfaces with two different network points, operating between producers and consumers of data. There is no set definition on how close the server must be to either endpoint, so there are four types of edges:
- Device edge (the server is a component within the end-user device).
- On-prem edge (nodes physically located in the local network or facility).
- Network edge (network-specific nodes such as base stations or telco data centers).
- Regional edge (the server is in a traditional local data center).
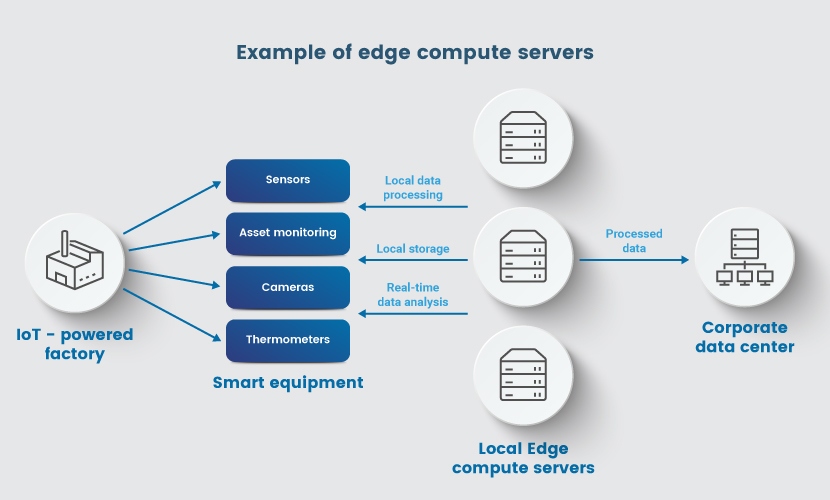
Here is an example of how an edge compute server that sits between IoT devices in a factory and the enterprise data center works:
- Various IoT devices on the factory floor (cameras, thermometers, sensors, etc.) interact with and send data to local edge compute servers.
- Servers provide local processing, storage, and data analysis to give visibility into production.
- If an IoT sensor registers, for example, a risky increase in a machine's temperature, the edge server recognizes the issue in real-time.
- The edge server stops the production before the machine overheats.
- The edge compute server sends relevant processed data to a corporate data center where humans can make a maintenance plan.
In this example, the edge server significantly reduces bandwidth to and from the corporate data center. Without the server, the data center would receive unprocessed data directly, causing latency that can lead to equipment damage or a fire.
Edge Server Use Cases
An edge server is a good choice for most use cases that require fast real-time data processing. These devices are also an excellent fit for use cases in which you cannot deploy standard, bulky servers. Here are some examples of how companies put edge servers to use:
- Servers within IoT sensors on industrial equipment.
- Surveillance sensors that have a local server for real-time data analysis.
- An app that streams movies and TV shows through an edge server with cashed videos.
- Hybrid cloud architecture in which centralized computing handles compute-intensive workloads while an edge server addresses workloads that need real-time processing.
- A banking app that uses an edge server for quick performance but isolates sensitive data on the origin server.
- IoT devices that perform in-hospital patient monitoring.
- Edge servers that provide remote monitoring of oil and gas assets.
- Self-driving cars that collect large volumes of data and make decisions in real-time.
Our software-defined edge computing servers are an ideal choice for any use case with low-latency and real-time processing demands.
New Bare Metal Cloud Edge location launched in Austin, Texas!
Advantages and Disadvantages of Edge Servers
Like most technologies, edge servers have specific benefits and drawbacks. Let us examine the pros and cons of edge servers in more detail.
Advantages
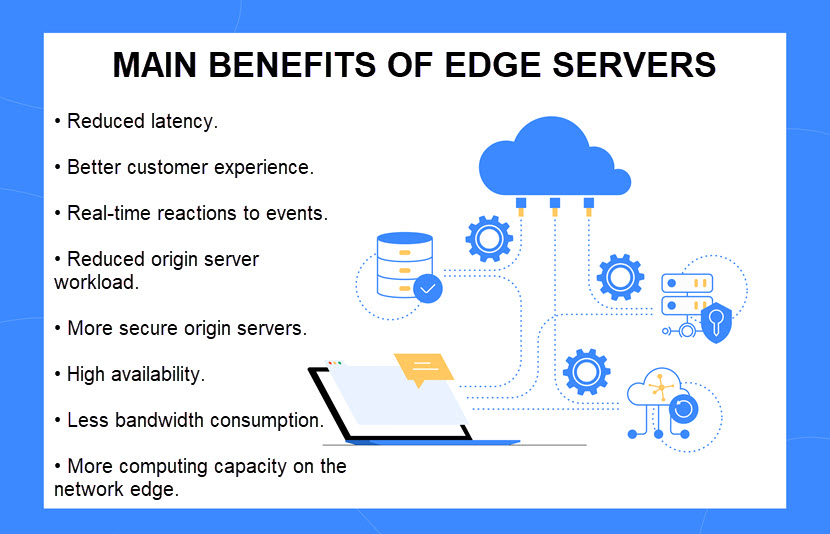
Here are the main benefits of using an edge server:
- Reduced latency: End-users experience better performance and faster loading times when they request content from a geographically closer server. In an industrial setting, the lack of latency means IoT and AI-powered devices can make split-second decisions and immediately respond to a risky situation.
- Reduced origin server workload: Sudden traffic spikes can impact the performance of an origin server. As a CDN server takes on most client requests in a region, your origin server is less likely to experience performance issues.
- Increased origin server security: A CDN edge server hides the origin server's IP address and proxies requests from clients. This networking model improves data integrity and privacy while reducing the origin server's exposure to DDoS attacks.
- Reduced bandwidth requirement (and cost): An edge server reduces the need to exchange data with external networks. This capability leads to lower network bandwidth requirements and reduced costs.
- Better data security: Fewer data transmissions to external locations and shorter times in transit mean fewer open connections and opportunities for cyberattacks. Also, since you no longer store or process data on a centralized system, you limit the consequences of a successful data breach.
- Better availability: Even if the origin server goes down, edge servers can maintain the functions in the local network. This capability is good for customer experience but vital for healthcare apps and critical control systems.
- Greater computing capacity: Edge servers provide computing capabilities that supplement limited local devices.
Read about the benefits of dedicated servers and see why sharing hosting resources with other tenants is usually a bad idea.
Disadvantages
There are also some downsides to using edge servers. If you are considering deploying an edge server, you should keep the following disadvantages in mind:
- Challenging maintenance: Since edge servers operate in different geographic locations, companies must define processes for monitoring, maintaining, and updating their equipment. Handling these tasks in-house is challenging, while outsourcing server management leads to additional costs and coordination challenges.
- Bigger attack surface: While edge servers offer security boosts in some areas, more servers mean more potential entry points into the network. Failing to maintain one of the edge servers properly can expose you to data leaks or breaches. Also, security risks on a local level (such as inexperienced teams and weak passwords) complicate cybersecurity.
- Not ideal for risky workloads: Securing data in transit over a network is typically easier than securing data during processing. Edge servers are unsuitable for high-risk workloads, sensitive data, or processes with unique compliance requirements.
- Problems with high data volume: Workloads with extreme data volumes can impact the performance of an edge server. If you have a workload that generates vast amounts of data, it is likely cheaper and easier to move the data to a data center or public cloud.
- High cost: Deploying and maintaining numerous geographically dispersed servers is costly. Not only do you need to purchase hardware, but you also require advanced infrastructure and a skilled team to get the most out of the edge.
- Data loss risks: Many edge servers discard irrelevant data after collection to handle high volumes of info. If the server discards relevant data by mistake, there is typically no way to retrieve the lost info.
Our article on edge computing challenges goes in-depth into the problems of edge servers and, more importantly, how to solve these issues.
The Future of Edge Hardware
Here is a quick overview of what you can expect to see from edge servers in 2022:
- Hardware-as-a-service: "As-a-Service" business model for edge hardware will continue to rise in popularity as companies look to eliminate upfront investments in edge equipment. We expect growth of both the subscription and consumption-based models, plus an increase in managed services for edge hardware.
- Convergence of storage and compute resources: Converged infrastructure enables a piece of hardware to have both storage and compute resources. Companies with ultra-low latency use cases will continue to push towards computational storage to reduce the amount of data moving between the library and compute plane.
- Breakthroughs in 5G: Edge servers will continue to help telco companies handle 5G traffic. An edge server near a cell tower will be vital for developing low-latency use cases such as smart cars and cameras.
- Fit with hybrid cloud: Edge hardware will continue to push companies towards hybrid cloud solutions. Edge servers are a natural fit with the hybrid cloud's "the best tool for the right job" mindset. They can also significantly improve the speed and reliability of a hybrid system.
- The rise of confidential computing: Besides at-rest encryption for local storage and in-transit protection, setting up confidential computing at edge hardware will become a priority as companies look for ways to protect data during processing.
PhoenixNAP's confidential computing enables you to deploy end-to-end encryption and ensure data remains safe at all times, both on-site and within edge servers.
Is Your Use Case a Good Fit for Edge Servers?
Edge servers have some unique challenges, but the benefits of edge computing are hard to ignore. You can uncover new business opportunities, improve operational efficiency, and provide a quicker, more reliable customer experience. These advantages outweigh any drawback, so you should definitely consider edge servers if your use case can benefit from local data processing.
Check out our article on IoT edge computing and the benefits of taking action on data as close to its source as possible to learn more.