Software Testing Methodologies and Models
Perfect software does not exist, and every program has potential failure points. Software testing is a software development lifecycle stage during which the team discovers unwanted errors in a program or system.
Different testing methodologies help pinpoint several types of software errors. Knowing how each software testing model works is essential to building, deploying, and maintaining a high-quality testing strategy and software.

Why Is Testing Important in SDLC?
The testing phase is a critical stage in the software development lifecycle. It comes after software implementation, and testing aims to discover and fix software errors.
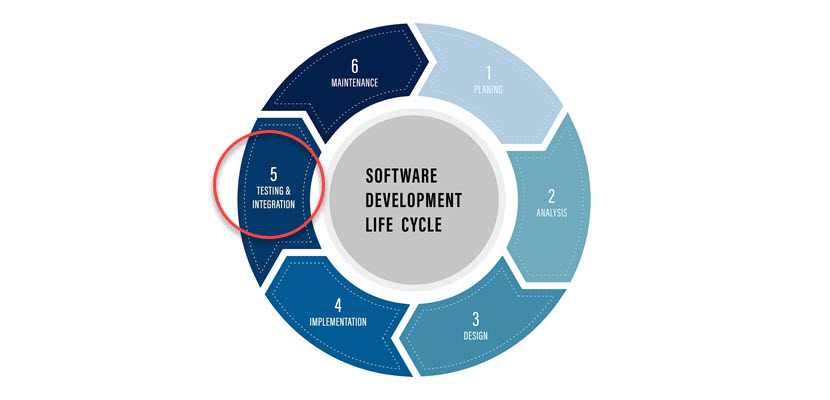
Software testing is crucial because the product goes into production after testing. Every software development team must deliver quality software for two reasons:
- The end user benefits from having a high-quality product built according to requests and specifications.
- The development team's integrity and the possibility of new projects depend on the software’s quality.
A software testing team performs various checks for different issues separately from developers. This approach aids in having a team solely focused on discovering problems and allows for implementing continual development.
Software Testing Methodologies
Software testing is a formal process performed by a testing team to help confirm a program is logically correct and valuable. Testing requires using specific test procedures and creating test cases.
Software testing is performed in two stages:
- Verification - Is the system built correctly?
- Validation - Is the system constructed according to the user requirements?
Software testing uses several methodologies and models to answer these two questions.
Black Box Testing
In the black box testing methodology, a program is a closed (black) box with unknown details. The only visible components to a tester are the program inputs and outputs.
A tester can determine whether a program is functional by observing the resulting outputs for various inputs. Black box testing does not consider a program’s specifications or code, only the expected behavior for different test cases. Black box testers do not necessary have to have be very skilled since they do not interact with any code.
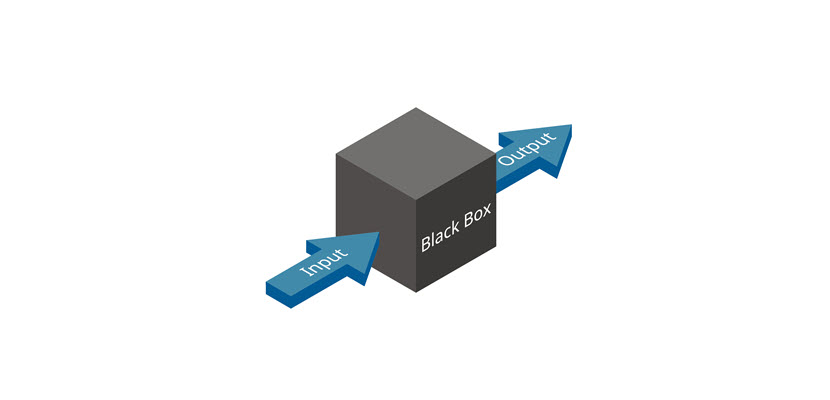
Black box testing comes with both benefits and drawbacks. The critical advantage of black box testing is there is no requirement to work with code and programming logic. However, testing for all input combinations is impossible.
Three types of tests are based on the black box testing methodology: functional testing, non-functional testing, and regression testing.
Functional Testing
Functional testing checks whether the software performs a specific function without considering which component within the system is responsible for the operation.
The testing team checks functionalities for both good and bad inputs. An example function is a user login page behavior. A functional test checks whether a user can log in with the correct credentials or not log in with incorrect credentials.
As the software’s complexity increases, so do the number of functions within the software. The order of testing functions is crucial for an efficient and functional testing strategy. As functionalities are often nested, the behavior of the software depends on the order of steps a person takes when using the software.
The main benefit of functional testing is that the testing team can check individual functionalities before all software components are completed. The probability of detecting errors in functional testing is exceptionally high, as it shows problems when using software from a user's perspective.
Non-Functional Testing
The non-functional testing method verifies software aspects apart from functionalities and features. This testing method focuses on how a program performs certain actions under specific conditions.
Non-functional testing helps uncover if a program is usable from a user's perspective. The method checks for usability issues, such as cross-compatibility across different devices, browsers, or operating systems.
Regression Testing
Regression testing is a software testing method that ensures all new code changes do not cause issues in previously tested components and negatively affect system stability. The testing method repeats tests from previous iterations, ensuring that the latest changes do not cause unwanted effects on existing code.
Regression testing is necessary after any program action which results in changes to the original code, such as:
- Implementing new requirements.
- Adding new functionalities to the program.
- Removing existing functionalities.
- Fixing any defects.
- Optimizing for better performance.
If software changes often, the best approach is to use automated testing tools and create reusable tests for multiple iterations and cycles of regression testing.
White Box Testing
The white box testing method is the opposite of black box testing. In this method, the program is an open (white) box whose inner workings are known to the tester.
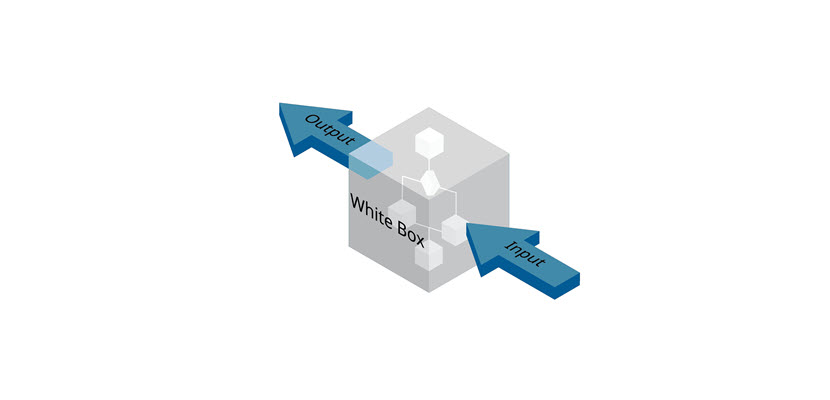
White box testing analyzes the source code and requires the following skillset:
- Coding and scripting knowledge.
- Familiarity with the specific programming language in use.
- The design of particular components.
Testers form a plan based on the program's structure. For example, white box testing can include creating scripted tests which go through the whole code and run every function. Specific tests can check whether there are infinite loops or cases where the code does not run.
The main drawback of white box testing is the number of test iterations, which increases as the the application becomes more complex. The method requires creating a strategy where recursions or loops execute fewer times for carefully chosen and representative values
Three types of tests are based on the white box testing methodology: statement testing, path testing, and branch testing.
Statement Testing
Statement testing is a testing technique within white box testing. The method assesses all executable statements in the code at least once. For example, if a code block contains several conditional statements, the statement testing technique involves going through all input iterations to ensure all parts of the code execute.
The statement testing technique discovers unused parts of code, missing referenced statements, and leftover code from previous revisions. As a result, statement testing helps clean up the existing code and reduces redundant code or adds missing components.
Path Testing
Path testing creates independent linear paths throughout the code. The testing team creates a control flow diagram of the code, which aids in designing unit tests to evaluate all code paths.
Analyzing different paths helps discover an application’s inefficient, broken, or redundant flows.
Branch Testing
Branch testing maps conditional statements in the code and identifies the branches for unit testing. The branch types are:
- Conditional: Executes when a condition is fulfilled.
- Unconditional: Executes regardless of any circumstances.
For example, the following code contains several nested statements:
if condition 1:
W
else if condition 2:
X
Y
else:
Z
A tester identifies all conditional branches. In the example code, conditional branches are W, X, and Z because the statements only run under a specific condition. On the other hand, Y is an unconditional branch because it always executes after the X statement.
Branch testing aims to execute as many branches as possible and test for all branching conditions.
Note: Check out our article on Black Box Testing vs White Box Testing to learn more about the differences between these two testing methodologies.
Functional Testing
Functional testing is a subtype of black box testing which considers the software specifications for a given function or program. The testing method provides various inputs and analyzes the outputs without considering the internal software structure.
Functional testing involves 4 distinct steps that start from more minor parts of the code and branch out into evaluating the entire system. The model aims to analyze a component or the program's compliance and check whether a system does what it is supposed to do according to specifications.
Step 1: Unit Testing
Unit testing is a software testing methodology that validates individual parts of source code. A unit test helps determine the functionality of a particular module (unit), and the process isolates individual parts to decide whether they function correctly.
A unit is an individual function, procedure, or object-oriented programming class. Typically, unit testing helps validate the front-end interface.
The main benefit of unit testing is early problem discovery in the development lifecycle. In test-driven development, such as scrum or extreme programming, testers create unit tests before any code exists.
The main drawback when applying unit testing is the need to evaluate complex execution paths in a program. Unit tests are localized and incompatible for discovering integration or system-wide errors.
Step 2: Integration Testing
Integration testing is a phase that comes after unit testing. The method combines previously assessed individual program units (modules) into larger groups and performs tests on the aggregates.
There are several different approaches to integration testing:
- The bottom-up strategy first evaluates and integrates low-level components before moving to more complex groups.
- The top-down approach uses reverse engineering to assess components from more complex groups and simplifies them into smaller units.
- Sandwich (hybrid) testing combines the bottom-up and top-down strategy by simultaneously testing low and high-level components.
- Big bang testing combines all components into a single large unit for testing. The method does not have an incremental approach compared to other testing methods.
Integration testing validates the connections between the front-end interface and an application's back end.
Step 3: System Testing
System testing performs tests on a completely integrated system. The step analyzes the behavior and compares them to expected requirements (Quality Assurance), validating a fully integrated software.
System testing aims to discover issues missed by integration and unit testing and to provide a comprehensive overview of whether the software is ready for release. The different testing approaches in system testing consider how well the software works in various environments and how usable the software is.
The main challenge of system testing is designing a strategy that fits within the available time and resource constraints while providing a comprehensive analysis of the entire system after integration.
Note: To easily scale out for testing purposes, we recommend using Kubernetes on BMC. It provides on-demand production-ready cloud-native environments.
Step 4: Acceptance Testing
The final part of functional testing is the acceptance test. The testing method aims to assess the approval of the application's end-user. The approach engages end-users in the testing process and gathers user feedback for any potential usability issues or missed errors during any previous testing phases.
Acceptance testing falls into one of the two following categories:
- User acceptance testing allows target users to evaluate and use the software through beta testing or a similar strategy. The user base determines whether the software operates as expected.
- Operational acceptance testing checks whether the software is functional and operates as expected. The test examines various software components, such as security, backup and disaster recovery, and failover testing.
After acceptance testing, the software is ready for production if the results meet the acceptance criteria. Otherwise, the software gets pushed back into previous development and testing phases if the testing does not pass the threshold.
Non-Functional Testing
Non-functional testing evaluates the software from the users’ perspective, focusing on the user experience. The testing methodology aims to catch any issues unrelated to a software's functionality but essential to the user's experience.
Non-functional testing considers parameters such as:
- Security
- Reliability
- Scalability
- Usability
- Availability
The focus of non-functional testing is on how a product operates rather than how it behaves in specific use cases. This testing model is conducted through performance testing, security testing, usability testing and compatibility testing.
Performance Testing
Performance testing checks the speed, scalability, and stability of the software. Several different performance testing subtypes exist, such as:
- Load tests check how the software functions under regular user demand.
- Stress tests examine how software behaves under a high user load or other complex circumstances.
- Spike tests check how software behaves under sudden high user load spikes.
- Endurance tests show an application's stability over an extended time.

All performance tests aim to catch and fix low latency and performance problems that degrade a user's experience.
Security Testing
Security testing checks for any security issues in software and is one of the most critical software testing methodologies. The method checks for any vulnerabilities within the system and possibilities of cyber attacks.
Methods such as penetration testing and vulnerability scanning help discover and lower security risks within the software, and there are also numerous penetration testing tools to automate the testing process.
Usability Testing
Usability testing evaluates how user-friendly and convenient software is to a user. The tests highlight how quickly an unguided user can do something in the program or application. The usability test results show how quickly a new user can learn to use the software and whether any interface improvements are necessary.
Compatibility Testing
Compatibility testing shows a system's behavior in various environments and with other software. The method focuses on integration with existing solutions and technologies.
Software Testing Models
The testing phase in the software development lifecycle is not the only place where errors can be identified and fixed. All development stages benefit from including software tests.
Continuous software development also requires continuous software testing. Software development should work with the testing team to discover potential problems early on or to determine places where testing is impossible. Early discovery is better, and as the steps progress, the cost of finding and fixing errors increases. According to the IBM System Science Institute, the relative cost of discovering and repairing defects in the maintenance phase is around six times higher.
Therefore, it is crucial to see how testing integrates into various software development processes and methodologies. Below is an overview of well-known software development models and how testing integrates into each method.
Note: Learn more about about continous software development, itnegration and testing in our CI/CD article.
Waterfall Model
The waterfall model is a software development method divided into sequential steps or stages. The team progresses to the following stage only after finishing the previous phase.
The testing team starts creating a test plan and strategy during the requirements phase in the waterfall model. Once the software goes through the implementation phase, testers verify if the software works correctly and according to specifications.
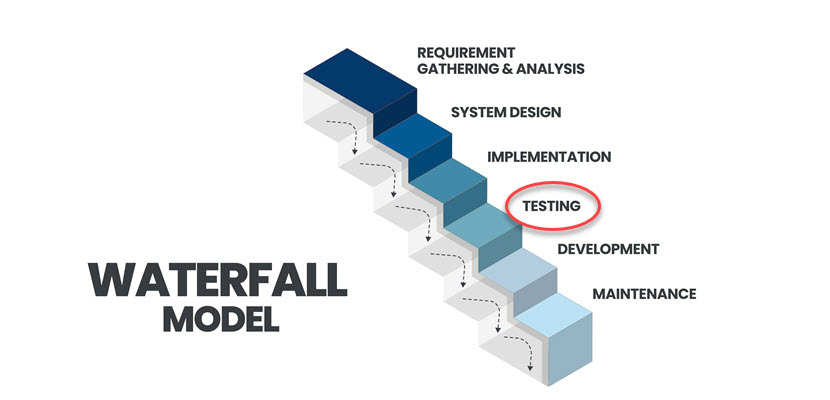
The main benefit of the waterfall method in software testing is that the requirements are well-defined and easily applied in the testing phase. The model is unfit for projects where conditions change often, and unplanned events occur.
Advantages
- Simple: A high level of abstraction simplifies the communication process with the end user, who does not need to know the technical process details to participate in the development process.
- Easy to follow: Project managers have access to critical points in project development, which allows them to be aware of the level of progress during development.
- Easy to apply: The model goes through a single iteration, which is convenient for replacing existing solutions with new software.
Disadvantages
- No feedback loop: The waterfall model lacks a feedback mechanism and multiple iterations. Defining all requirements at the start of the project is impossible and returning to any previous step to make changes is not a supported path in the model.
- No apparent connection between phases: The model assumes that every previous development phase is the input for the following step. However, the model does not define how requirements transform into a design.
- Not focused on problem-solving: The waterfall model approaches software design as a hardware or production mechanism. On the other hand, software design requires testing and trying different approaches. The model limits any modular and creative process during software development.
- Limited end-user interaction: The waterfall model communicates with a user only in the first step of the development phase and in the final stage when the product is complete. The approach limits user interaction, which makes the development process inefficient.
V Model
The V model is an extension and improvement of the waterfall model. The model divides into sequential steps, with additional testing steps for each development phase. The V model goes through all the stages in functional testing to verify and validate the software.
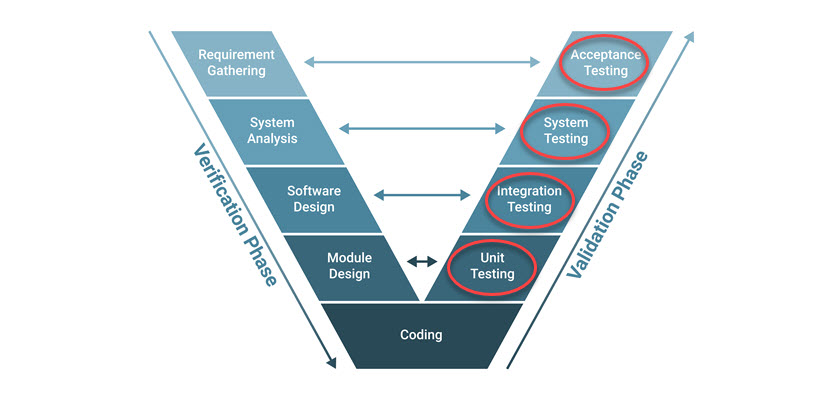
The shape of the V model shows the corresponding test phases to the development life cycle phases. When viewed left to right, the model demonstrates the order of steps as time progresses, while viewing from top to bottom reveals the abstraction level.
Advantages
- Feedback mechanism: The V model is practical for simple and complex projects due to the possibility of returning to any of the previous phases.
- Verifies and validates: The model allows checking whether a project is developed well, fully implemented, and fulfills the user requirements.
- High-quality products: The development process is well-organized and controlled, guaranteeing the software's quality.
- Testing in early phases: The testing team participates in the early development phases, which results in a better understanding of the project from the start. The model significantly saves time and resources on testing in the later stages of development.
Disadvantages
- Not flexible: When problems appear, the team must update all phases must adapt to the software changes and be updated, including the documentation. Any change slows down the development process.
- Costly: Implementing the V model requires significant resources to support numerous development teams. The model is better suited for larger projects and businesses.
Agile Model
The agile methodology is a fast and iterative approach to developing software that follows the principles defined in the Agile Manifesto. It breaks down software development into small increments and multiple iterations. The agile model allows constant interaction with end users, and requirements change constantly.
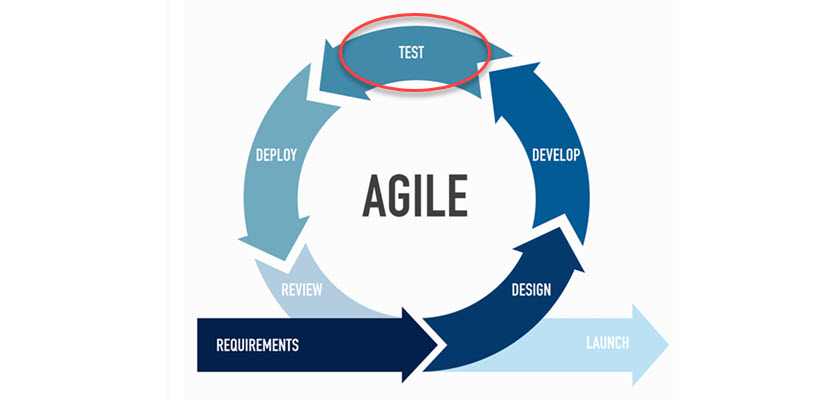
Testing in the agile model happens in every iteration. Software testing in this environment requires applying continual testing into the CI/CD pipeline through automated testing tools and testing frameworks.
Advantages
- Fast development: Deploying software happens quicker than in other models. The model is adaptive and responsive to changes, resulting in shorter turnaround times.
- Smaller iterations: Errors and defects are easier to spot and analyze in smaller chunks. Delivering software takes less time, and new iterations happen often.
- High level of user interaction: Constant end-user feedback ensures acceptance testing happens often. As a result, the product is closer to the requirements with each iteration.
Disadvantages
- Unpredictable: Although the testing team gathers user feedback, there is no guarantee the next iteration will contain these changes. The fast pace creates an unpredictable product roadmap.
- Costly: Continual releases to production and development result in higher expenses. Predicting the necessary effort for each change becomes difficult.
- Phase overlap: Every iteration goes through all the development phases. As sprints progress, it becomes trickier to distinguish who is responsible for which task.
Scrum Model
The scrum model is a project management approach that uses principles from the agile model. The model is goal-oriented and time-constrained into iterations known as sprints. Every sprint consists of meetings, milestones, and events managed by a scrum master.
The scrum model does not feature a testing team, and developers are responsible for constructing and implementing unit tests. The software is also often tested by the end user in each sprint.
Some scrum teams do feature testers, in which case testers must provide time estimations for every testing session during scrum meetings.
Advantages
- Fast-paced: The scrum model ensures project delivery happens quickly, which makes it suitable for fast-paced projects under development.
- Cost efficient: Every sprint consists of several members, and the fast-paced environment ensures the project completion happens within a specified time frame.
- High-level of user interaction: Like the Agile model, scrum releases code often, which results in constant user interaction. Continual feedback results in satisfying user requirements through every sprint.
Disadvantages
- High chance of failure: The scrum model requires a high level of interaction and commitment. Daily meetings are stressful, and one team member leaving impacts the whole project. The software is at a higher risk of failure in a non-compliant team.
- Lacks quality: When a model lacks a testing team, the quality of the software is unacceptable. The resulting software is of lower grade than those undergoing intensive testing.
DevOps Model
The DevOps model combines continuous testing into every development stage, while also having a dedicated testing role in the team. The goal of testing in the DevOps pipeline focuses on software quality and risk assessment.
Automated testing and test-driven development improve code reliability, which help minimize the probability of new builds from breaking existing code.
Advantages
- Fast software delivery: DevOps improves the delivery speed for new features and bug fixes. Quick response times to issues improves customer satisfaction with the product.
- Quality software: Automated testing and continuous deployment improve software quality. DevOps ensures every change is tested before deploying software to production.
- Error efficient: Integrating testing in the initial stages of development avoids having to fix problems later in the development cycle.
Disadvantages
- Difficult to implement: DevOps requires integrating development with operations and a following DevOps principles, which is hard to achieve in large organizations with complex systems.
- Increased risks: DevOps heavily relies on automation, which leads to problems if not configured properly. Issues are difficult to track down when they do occur.
- Excessive costs: The model requires significant investments into infrastructure and DevOps tools. A misconfigured system creates integration challenges which are difficult to manage.
Learn how to set up a test sandbox environment you can easily scale for production workloads.
Iterative Development
Iterative development divides software development steps into subsystems based on functions. The method is incremental, and each increment delivers a completed system. Every new iteration improves existing processes within every subsystem.
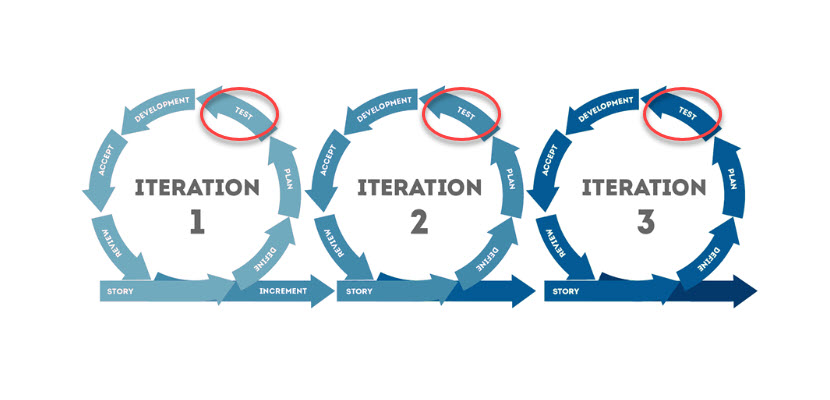
Early releases provide a primitive version of the software, while every following release improves the quality of the existing functionalities. Testing is simpler in early phases and increases in complexity as iterations progress.
Advantages
- Risk control: Iterative development allows starting with high-risk tasks first. The controlled nature of the development method enables improving any issues through iterations.
- Easy to follow: Every iteration shows an improvement from the previous. Measuring changes between iterations becomes simple for project managers.
- Early training: Since iterative development delivers a simpler version of the full software, users are engaged and use the software early. User feedback is based on the whole system, and improvements are simpler to implement in the following iterations.
- Specialized versions: Versioning software becomes simple, as development teams can focus on specific improvements with each iteration. For example, one iteration improves the user interface, while the following iteration improves the software's performance. The approach simplifies the test design process.
Disadvantages
- Costly: Every iteration requires the presence of the whole software development team.
- Lacks full specifications: The iterative development approach starts creating a system from simple requirements. As time progresses, the conditions also change. The fluidity of specifications makes it challenging to see when the project ends.
- Hard to manage: Iterative development requires intense project management and risk assessment for each iteration. As projects grow, the system's complexity increases.
Spiral Model
The spiral model is an agile model with a focus on risk assessment. The model combines the best qualities of the top-down and bottom-up development methods. The method uses the waterfall model phases as increasingly complex prototypes.
As risk analysis is the focus of every step, the spiral model enables the early discovery of faults and vulnerabilities. The model performs an early assessment of issues, which makes security testing less costly in the long run.
Advantages
- Flexible; The spiral model is adaptable to requirements changes, even after developing a feature. There is less strain on the testing team when reporting issues.
- Secure; Risk analysis is in every step of the development process, and the iterative approach also helps manage risk. The spiral model focuses more on software security compared to other development models.
- High level of user interaction; The iterative approach in the spiral model allows engaging the customer in the development process and receiving continual feedback. The development team quickly makes changes during development, which saves costs and resources in the long run.
Disadvantages
- Costly: The spiral model best suits large projects and complex software.
- Specialized risk analysts: The model depends on having high-quality risk analysts included in every development step for efficient risk assessment.
- Complex: The model is hard to follow and requires an increased focus on protocols and documentation in every step of development.
- Time management: The duration of each phase is unknown. The model is susceptible to exceeding the budget and falling behind on time constraints.
Note: Learn more about the Automated Security Testing Best Practices.
RAD Model
The RAD (Rapid Application Development) model is an agile methodology that combines prototyping with iterative development. The method focuses on gathering user requirements, while the rest of the development process has no specific plan or steps.
RAD is a fast-paced technique that focuses on creating reusable components that serve as templates for following projects or prototypes. The testing team assesses all prototypes in every iteration and immediately integrates the components into the final product.
Advantages
- Flexible: The model quickly implements requirements changes and accommodates new user requirements.
- Reusable: Creating reusable prototypes provides a templating approach to development, increasing code reusability and requiring less effort in the long run.
- Fast: The development time and short iterations enable continual software integration and rapid delivery. The RAD model incorporates various automation tools to speed up the development process.
Disadvantages
- High expertise dependency: RAD-based teams are small, highly skilled, and technically strong. The RAD model requires an experienced team of developers to identify and model user requirements.
- Only suitable for modular systems: Not all software has clear-cut components. RAD requires creating smaller prototypes which are reusable. Complex systems require specialized features which do not apply to all use cases.
Extreme Programming
Extreme programming (XP) is an agile method for developing software best suited for small to medium-sized teams (6-20 members). The technique focuses on test-driven development and short iterations that provide users with direct results.
XP has no strict methodology for the development team to follow. Instead, the method provides a flexible framework where procedures or the sequence of steps changes depending on the activity. The Agile Manifesto principles, and techniques like pair programming, are vital components in XP.
Advantages
- Focus on software development: The team creates software rather than focusing on meetings and documentation. The work environment is comfortable for developers, with many opportunities to learn and improve skills.
- Short development time: The lack of rules and procedures makes the software delivery speedy. Quick results are beneficial to customers.
- Test-driven development: Unit tests exist before writing code, and programmers know what is tested before creating software. This approach stimulates programmers to take better precautions while coding.
Disadvantages
- Hard to implement: The method is tough to implement. XP requires programmers with strict discipline who accept and follow the required principles and can work together closely.
- Client dependent: The client chooses whether to participate in the development process. A non-participating client often leads to unsatisfactory software.
Conclusion
High-quality software testing is what differentiates between quality software and a lackluster project. The importance of software testing is crucial to development, which is why there are so many testing methodologies and approaches. Development teams should follow trends in software testing and be ready to fundamentally change their approach to profit from new software testing methodologies and models.
Next, check out how automated testing frameworks help streamline the testing process and improve testing speeds during the testing phase.