What is Network Infrastructure Security?
A robust network infrastructure security is a prerequisite for efficient business communication, productive teams, and safe operations. Without proper measures, the networking infrastructure may become an exploitable weakness that leads to data breaches, poor user experience, costly setbacks, and long-lasting brand damage.
This article is an introduction to network infrastructure security. Read on to learn about the benefits and the means of protecting your company's networking devices and software.
What Is Network Infrastructure Security?
Network infrastructure security is a set of measures and processes that protect a network's underlying hardware and software. Every network setup requires a unique mix of defensive measures, but most companies rely on:
- Strict access controls and authentication protocols.
- Firewalls.
- Virtual private networks (VPNs).
- Behavioral analytics.
- Data encryption (at rest, in transit, and in use).
- Intrusion detection systems.
Each device and system running a network is a potential entry point for an intruder. Network infrastructure security aims to deny unauthorized access and prevent an attacker from modifying, deleting, controlling, or stealing network resources.
This branch of cybersecurity protects all devices responsible for network communications, including:
- Routers.
- Switches and cables.
- Dedicated servers.
- LAN cards.
- Load-balancers.
- Domain name systems (DNS).
- Endpoints (employee workstations, laptops, mobile devices, tablets, printers, etc.).
Network infrastructure security also protects networking software, including:
- Network operations and management systems.
- Apps for network security.
- Operating systems on networking devices.
- Networking services (T-1 lines, IP addressing, satellite, DSL, wireless protocols, etc.).
While network infrastructure is primarily vulnerable to external attacks (denial-of-service attacks, unauthorized access, spam, ransomware, man-in-the-middle attacks, malware, etc.), companies also need to consider insider threats. The most common examples of internal dangers are:
- Intentional deletion or modification of data.
- Device theft or sabotage.
- Data leakage (whether malicious or unintentional).
- Accidental downloads of malicious content.
An excellent first step to protecting your network and its infrastructure is deploying one (or several) of the market's top network security tools.
How Does Network Infrastructure Security Work?
Network infrastructure security requires a holistic approach that combines best practices and ongoing processes to ensure the underlying infrastructure always stays safe. What security measures a company deploys depends on:
- Relevant legal obligations.
- Industry-specific regulations.
- The unique network and security requirements.
You can run a network security audit to get a better sense of a network's weaknesses and needs. For even more detailed analysis, you can rely on vulnerability assessments or organize a penetration test.
Once a company understands its network needs, the organization can perform some (or all) of the best practices explained below. In addition, companies can also rely on some universal standards, such as data encryption, strong passwords, top facility security, and data backups.
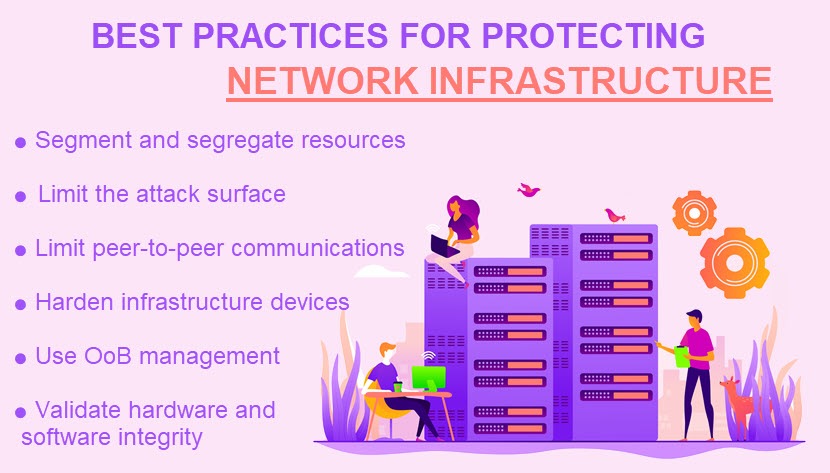
Segmentation and Segregation of Network Resources
Network segmentation is the process of breaking a network up into smaller segments with individual firewalls, access controls, and security protocols. This tactic allows an admin to group infrastructure resources (apps, servers, routers, etc.) into subnets based on security issues, overall risk, and system criticality.
While network segmentation cannot prevent an attack, the process reduces the impact of a successful breach. Segmentation stops an intruder from:
- Spreading a malicious file or package across network systems and devices.
- Reaching sensitive data from a single compromised host.
- Moving laterally through the network infrastructure.
- Launching a network-wide cyberattack.
In addition to segmentation, companies should also segregate network resources based on role and functionality. Segregation enables an admin to separate critical network segments from the Internet and other internal, less crucial subnets.
Refer to our article on network segmentation to learn more about the effects and benefits of breaking a network up into smaller subnets.
Limitation of the Infrastructure's Attack Surface
The network infrastructure's attack surface is the sum of the networking elements an intruder can attack and cause a security incident. Common attack surface elements are:
- Servers.
- Networking applications.
- APIs.
- Routers.
- Endpoint devices.
- Network admins.
A company can rely on the following tactics to reduce the infrastructure's attack surface:
- Uninstall and remove all unused network devices, apps, and services.
- Monitor all third-party components and services for vulnerabilities.
- Keep networking software up to date with the latest patches and updates.
- Implement the principle of least privilege to network servers, apps, databases, etc.
- Segregate all critical systems and apps.
- Implement a multi-factor authentication system.
Before you start reducing the infrastructure's exposure, you should first map the attack surface. Network admins should maintain an up-to-date list of all network assets, versions, and interlocking (Censys and Shodan are two excellent tools for attack surface mapping).
Check out our post on attack vector vs attack surface to learn more about these key security concepts.
Removal of Unnecessary Peer-to-Peer Communications
Allowing unfiltered peer-to-peer communication (such as workstation-to-workstation or router-to-router) creates serious infrastructure weaknesses. If an intruder breaches a host, lateral communication enables attackers to get a foothold within the network and reach additional resources.
To counter this threat, a company can:
- Restrict communications with host-based firewalls that deny the flow of packets from peer hosts.
- Implement a VLAN access control list (VACL), an additional filter that controls access to and from VLANs.
Learn about zero-trust security, a highly effective strategy of preventing intruders from quietly expanding across the network.
Protect Infrastructure Devices
Hardening devices is vital to network infrastructure security. Admins can implement some (or all) of the following practices to harden a device:
- Disable unencrypted remote admin protocols for managing network infrastructure (Telnet, FTP, etc.).
- Use SNMPv3 (or newer versions) for network management.
- Disable unnecessary services on routers and switches, such as discovery protocols, source routing, HTTP, SNMP, Bootstrap Protocol, etc.
- Set up and maintain a reliable system for log monitoring.
- Limit administrative privileges for infrastructure devices.
- Protect access to the console and virtual terminal lines.
- Restrict physical access to routers, servers, and switches.
- Control access lists for remote administration.
- Back up all configurations and store them offline.
- Ensure all network devices have the latest OS patches.
Read our article on cybersecurity best practices for more ideas on how to protect your business from both external and internal threats.
Out-of-Band Management (OoB)
OoB management allows an admin to use alternate communication paths to manage network devices remotely. A company can implement OoB physically or virtually (or through a hybrid of the two):
- Investing in extra physical hardware can be expensive, but that approach is typically the more secure option.
- Virtual implementation is less costly but requires significant configuration changes and post-setup administration.
Good practices when setting up OoB management are:
- Segregating standard network traffic from management traffic.
- Ensuring that management traffic on devices comes only from OoB.
- Applying encryption to all management channels.
- Encrypting all remote access to infrastructure devices (such as terminal or dial-in servers).
- Managing all administrative functions from a dedicated, fully patched host over a secure channel.
Using OoB to manage the network infrastructure strengthens security by limiting access and separating users from network management traffic. OoB also helps with security monitoring and prevents an intruder from discovering configuration changes.
Hardware and Software Integrity Validation
Illegitimate hardware and software can be a severe risk to network infrastructure. Gray market products introduce threats as they likely did not go through quality standard tests. To properly validate hardware and software in the network infrastructure, a company should:
- Purchase only from authorized vendors and resellers.
- Define and enforce regular processes for verifying and monitoring network hardware and software.
- Maintain direct and strict control of the supply chain.
- Inspect all devices for signs of tampering before and following installation.
- Validate serial numbers from multiple trustworthy sources.
- Download updates and patches only from official websites.
- Train staff members to increase awareness of gray market devices.
Products from the secondary market also carry the risk of acquiring counterfeit, stolen, tempered, or second-hand devices.
The Importance of Network Infrastructure Security
Network infrastructure is a common target both for novice and experienced hackers as network equipment typically has many vulnerabilities. The usual weaknesses are:
- Large attack surfaces with numerous entry points.
- Many targets for social engineering attacks.
- Lack of employee awareness for cyber threats.
- Various security flaws due to constantly evolving needs and setups.
- Poorly protected devices (especially at small and home-based offices).
- Numerous unencrypted and legacy protocols.
- Admins who do not change vendor default settings, harden devices, or perform regular patching.
These weaknesses make network infrastructure a go-to target for a malicious actor aiming to use a compromised device to monitor, modify, and deny traffic to and from the company.
Once an attacker gains control of the network infrastructure, there is not much the intruder cannot do. The most common objectives are going after sensitive data, collecting intel, installing ransomware on as many devices as possible, and sabotaging resources.
PhoenixNAP's Global Network enables you to securely connect and deploy your environment across multiple platforms and locations while enjoying superior connectivity and 100% uptime.
Types of Network Infrastructure Security
Companies can rely on a variety of approaches when protecting networking software and equipment. The most common types of network infrastructure security are:
- Access control: The virtual or physical prevention of unauthorized users, apps, and devices from accessing network hardware and software.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): A VPN encrypts connections between two network endpoints, creating a secure path of communication over the Internet.
- App security: App-specific measures an admin installs to lock down potential weak points.
- Firewalls: A gatekeeping device or program that allows (or prevents) traffic from entering or leaving the network.
- Anti-virus programs: These solutions monitor, identify, and eliminate software-based threats. Besides viruses, an anti-virus program also protects from adware, keyloggers, spyware, URL threats, spam, and phishing attacks.
- Behavioral analytics: A BA tool automatically analyzes network activity and detects suspicious behavior.
- Wireless security: A system dedicated to keeping intruders out of a wireless network.
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS): These systems monitor for, record, and report any potentially dangerous activity within a network.
- Intrusion prevention systems (IPS): Besides monitoring and reporting malicious activity, an IPS can also automatically respond to a threat with a scripted response plan.
While you will likely not need every security measure listed above, a company should rely on multiple approaches to broaden its network infrastructure defense.

Read about different types of network security a company can deploy to ensure network activities stay reliable and safe.
Benefits of Network Infrastructure Security
The main benefit of network infrastructure security is that the company can reliably control and defend the underlying hardware and software running the network. However, improving network infrastructure security also provides other advantages:
- Better network performance: Reliable infrastructure increases uptime and improves network performance. Companies also enjoy faster time-to-market, more predictable expansions, and consistent app performance.
- Secure BYOD: Bring-your-own-device is growing in popularity as companies look to capitalize on the benefits of relying on employee-owned devices. A high-level network infrastructure security ensures the company can identify any BYOD-related issue or threat in real-time. The same applies to all personal devices an employee brings to the workplace.
- Quickly identify improperly used assets: A network asset may be unnecessarily in use in one place but critically required in another. Proper infrastructure monitoring can quickly identify this problem and redirect resources instead of wasting money to compensate for that imbalance.
- Limited blast radius: If an intruder breaches the network infrastructure, security protocols immediately inform the defense team. The malicious actor has less time to do damage, and the network will stop any attempt at lateral movement.
- Improved bandwidth use: Robust network infrastructure security leads to solid management of network bandwidth capacity. Companies save money by quickly identifying flow characteristics, including how much bandwidth is in use at any time and for what purpose.
To reduce data transfer costs even further, you can deploy pNAP's Bare Metal Cloud and use one of the offering's cost-effective bandwidth packages.
Challenges of Network Infrastructure Security
Besides the initial investment, there are no significant downsides to improving the protection of network infrastructure. However, there are several challenges you should know about when improving network infrastructure security:
- Centralizing traffic can be difficult if there are multiple different subnets and business sites. Network visibility, monitoring, and management can also be challenging in that scenario.
- Removing duplicate data is vital to the effectiveness of network infrastructure security. If solutions process too much duplicate data, defenses may become less effective in detecting threats.
- If a company relies on several cybersecurity providers, ensuring the system sends the correct data to the right tool can be complex.
These difficulties aside, the biggest challenge of maintaining high levels of infrastructure security is a careless or uninformed employee. As with most security efforts, people are the weakest link, so ensure your staff members:
- Understand cybersecurity best practices.
- Know the importance of keeping the network infrastructure safe.
- Understand how the company protects networking devices and software.
- Know what to do if they detect suspicious activity.
Regular cyber security awareness training is the most efficient method of ensuring employees do not become an exploitable link in your security strategy.
A Must for Any Cybersecurity-Aware Organization
A robust infrastructure reduces operational costs, improves productivity, and keeps sensitive data away from intruders. While no security strategy will stop 100% of attack attempts, network infrastructure security can minimize the fallout after a cyberattack and ensure you get operations back online as quickly as possible.