What Is HPC (High Performance Computing)?
Some workloads, such as DNA sequencing or seismic analysis, are simply too immense, time-consuming, and complex for a single computer to process. High performance computing (HPC) enables us to create an IT environment specifically for these compute-intensive workloads, paving the way for the level of data analysis we never had before.
This article is an intro to high performance computing and the impact this cutting-edge tech promises to have on the way we do business. Read on to learn what HPC is, how these systems work, and why high performance computing promises to push the boundaries of enterprise IT.

What is High Performance Computing?
High performance computing (HPC) is the practice of performing data calculations at incredible speeds by using multiple compute servers that work in parallel. These groups of servers (clusters) can have hundreds or even thousands of interconnected computers (nodes) that work simultaneously on the same task.
To put it into perspective, a standard desktop with a 3 GHz processor can perform around 3 billion calculations per second. An average HPC system can perform quadrillions of calculations per second.
While not every system requires an extreme processing speed, HPC is essential for advanced, time-consuming use cases that rely on:
- Big data and massive multi-dimensional datasets.
- Real-time data analytics.
- Extreme performance databases.
- Advanced machine learning and AI elements.
A casual user does not have much use for high performance computing. Instead, the prime adopters of HPC are organizations that work with extreme amounts of data and run CPU-heavy apps. Here are a few exciting examples:
- Analyzing disease progress of millions of patients to discover insights and sickness patterns.
- Running a car crash simulation without having to test a vehicle physically.
- Analyzing millions of credit card records to identify fraud attempts.
- Simulating the impact of airflow on the wings of an airplane.
- Identifying next-gen materials (e.g., for better batteries or more resilient buildings).
Not long ago, the only users of high performance computing were state agencies, research institutions, and top-tier corporations. These organizations were the only ones that could afford to set up an HPC system on-site.
Nowadays, cloud computing has democratized HPC, so companies of all sizes can solve compute-heavy computational problems within reasonable time and cost parameters.
Read about quantum computing, a cutting-edge tech that relies on quantum mechanics to solve problems too complex for a classical computer. Like HPC, quantum computing performs data processing at speeds an ordinary device cannot achieve.
How Does HPC Work?
A standard computer performs tasks on a queue-based, transaction-by-transaction basis. An HPC cluster uses all available resources to complete as many tasks as possible at the same time.
In an HPC architecture, hundreds of nodes work in parallel to boost the processing speed. Once an engineer integrates and configures nodes, a distributed processing software framework (like Hadoop MapReduce) splits computing tasks evenly between all computers on the network.
There are three hardware and system designs that enable an HPC system to provide high processing speed:
- Parallel computing: This technique allows hundreds of processors to run calculations at the same time.
- Cluster computing: Cluster computing enables an admin to set up a collection of computers that work together as a single resource. Such a system must have a scheduler that keeps track of available resources.
- Grid and distributed computing: This type of computing connects the processing power of numerous computers within a network (either at a single or across multiple locations).
Each component within an HPC system (computer, networking, storage, etc.) must keep pace with each other to offer peak performance. For example, the networking component must keep up with the speed of data moving between on-site servers and cloud storage.
You can run two types of workloads on an HPC system:
- Embarrassingly parallel workloads: An admin can divide these computations into small, simple, and independent tasks. Such tasks run at the same time with little to no communication between them.
- Tightly coupled workloads: These large workloads require you to break them into smaller tasks that must communicate during processing.
Depending on your use case, you can run HPC either on physical hardware or in the cloud (or both if you choose to set up a hybrid architecture). Either way, Linux is by far the most popular OS for HPC.

HPC Use Cases
Here is a list of use cases HPC can either speed up, improve, or flat-out make possible:
- Various FinTech use cases (automatic and high-frequency trading, AI-based credit card fraud detection, real-time tracking of stock trends, complex risk analyses, self-guided tech support, etc.).
- Predicting and tracking storms and other unusual weather patterns.
- Various healthcare uses (vaccine research, testing drugs and new cures, speeding up screening techniques, analyzing patient diagnoses, developing new therapies, studying disease patterns, etc.).
- Genomics use cases (sequencing DNA, analyzing drug interactions, running protein analyses, genome mapping, etc.).
- Oil and gas use cases (testing reservoir models, spatial analyses, locating new oil and gas resources, running a seismic or wind simulation, etc.).
- Flight training for pilots and simulations for airplane testing (e.g., airflow over the wings of planes or structural strength tests).
- Entertainment and media use cases (rendering special effects, live event streaming, transcoding media files, processing an AR or VR video game, real-time image analysis, etc.).
- Analyzing massive amounts of end-user data to improve customer service and find better fits for product offers.
- Discovering next-gen materials for batteries, buildings, semiconductors, etc.
- Running advanced blockchain programs.
- Government use cases (climate modeling, nuclear stewardship, space exploration, etc.).
- Retail use cases (inventory analysis, logistics and supply chain optimization, sentiment analysis, etc.).
- Life science use cases (molecular modeling, biology simulation, and protein docking).
No matter how compute-intensive your workloads are, pNAP's HPC servers can ensure you have enough processing power, storage, and memory to run your HPC use case.
Advantages and Disadvantages of HPC
All technologies come with pros and cons, and high performance computing is no exception. Let us look at the main advantages and disadvantages of HPC.

Advantages of High Performance Computing
Here are the primary advantages of HPC:
- Processing speed: The whole point of HPC is to provide fast processing, which is undoubtedly its biggest benefit. An HPC system performs extreme amounts of calculations in seconds, whereas a regular processor would take weeks or even months to complete the same task. HPC enables these speeds with cluster/parallel computing, the latest CPUs and GPUs, low-latency networking, and block storage devices.
- Reduced need for physical testing: You can use HPC to create simulations and minimize (or even outright eliminate) the need for physical tests. Whereas some teams use this advantage of HPC to save time, others (such as car manufacturers and airline companies) also cut costs by removing the need for building and destroying prototypes.
- Fault tolerance: If one node fails, the rest of the HPC system continues to run. Operations will slow down, but you will not suffer downtime.
- New business opportunities: HPC enables a company to run data-intensive workloads on a new scale. From product design to tracking patterns, HPC opens new possibilities that were never realistically available to an enterprise, let alone an SMB.
- Improvement of existing processes: The capability to crunch numbers and analyze data quicker also enables an admin to streamline current processes and tasks.
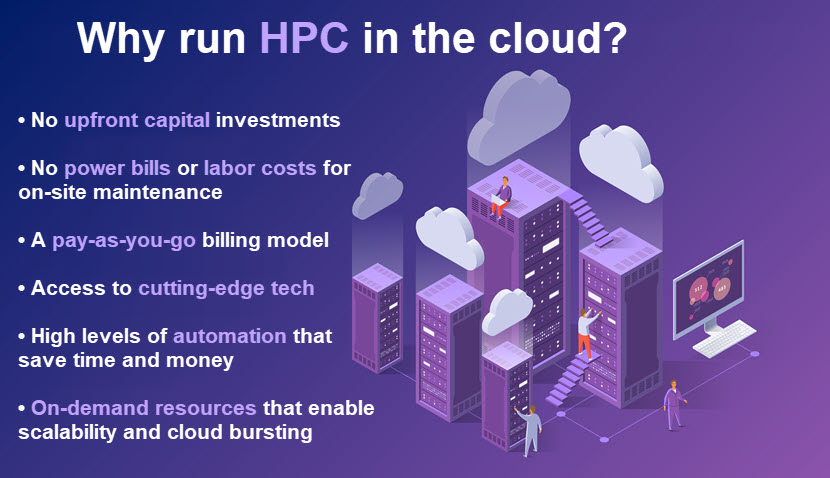
- Faster tasks lead to lower costs: HPC enables an app to run and get results more quickly. As a result, you save both time and money in the long run. Also, a cloud-based HPC system enables you to rely on a pay-as-you-go model that further reduces IT costs by cutting overhead expenses.
Whenever deciding whether to run something on-prem or in the cloud (HPC-related or otherwise), you must know the difference between capital expenditure (CapEx) and operational expenses (OpEx). Our CapEx vs OpEx article offers an in-depth breakdown of the two cost models.
Disadvantages of High Performance Computing
HPC offers something an ordinary business has never had before, but the technology does pose certain challenges. Here are the main disadvantages of HPC:
- High capital investments: If you decide to set up an HPC system on-site, be ready to set aside a hefty budget. Purchasing and maintaining hundreds of compute nodes is highly expensive. Expect high upfront costs of hardware, a capable technician team, and an on-prem data center.
- Ongoing costs: Maintaining a supercomputer comes with high cooling and power bills.
- Aging on-prem infrastructure: As on-prem HPC equipment ages, the system's performance will deteriorate. Unfortunately, a high number of nodes increases the chance one of them will fail, so you will have to continually fix an HPC system to keep it running at 100%. Also, keep in mind that hardware will likely be outdated in a few years, leading to even more costs.
- Lack of portability: Code developed for one HPC cluster will likely not work ideally on another system. Also, moving the entire HPC environment from point A to B can take weeks or even months.
- Challenging to run: Running an on-site HPC cluster is complex and time-consuming. Expect low employee retention rates or be ready to offer higher wages than other companies can afford to pay.
- Long purchasing cycles: You should also account for long purchasing cycles as HPC equipment is in high demand. Waiting around for hardware to arrive can slow down the pace of on-site research.
Most of these barriers to HPC do not exist if you rely on cloud computing instead of on-prem hardware. Our article on the advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing helps evaluate whether on-demand IT is the best choice for your business.
Future of High Performance Computing
Organizations across numerous industries are turning to HPC in pursuit of faster analysis of big data and next-gen simulations. As a result, experts predict that the HPC market's value will grow to US$44 billion by 2022 and US$50 billion by 2023.
In the following years, the tech will have the most immediate impact on the following verticals and use cases:
- Precision medicine.
- Fraud detection in FinTech.
- Personalized interest rates.
- Business intelligence.
- Seismic analysis.
- Customized marketing.
- Chatbots.
- Internet of Things (IoT).
- Smart cities.
- Self-driving vehicles.
- Deep learning and neural networks.
- Data warehouses.
Companies within these niches will rely on HPC to speed up research and innovation as they get to devote more computing power and capacity for their use cases.
Cloud computing will also play a massive part in the expected growth of the HPC market. Cloud-based HPC deployments relieve a business of the need to invest millions in data center infrastructure and ongoing operational costs. Moving HPC workloads to the cloud also:
- Decreases time to market.
- Enables users to ramp resources up or down to adjust to current IT needs.
- Provides access to the latest tech (newest and fastest CPUs and GPUs, low-latency flash storage, RDMA networks, and top-tier levels of cloud security).
Container technologies will also gain momentum in the HPC market. Relying on containers helps meet the needs of many HPC apps, such as scalability, reliability, automation, and security.
If you decide that outsourcing HPC is the way to go, you will have to find a reliable hosting facility. Our article on data center selection takes you through all you need to know to find a partner that meets all your hosting needs.
A Mainstay of Enterprise IT or a Passing Fad?
If you have a use case that genuinely requires HPC, there is no alternative to setting up a cluster. Luckily, cloud computing makes HPC more readily available and affordable than ever before, so businesses of all sizes can now use this cutting-edge tech. Until we figure out a new way to achieve HPC's processing speeds, high performance computing is undoubtedly here to stay.